Interim results of the B-YOND study evaluating long-term safety and efficacy of recombinant factor IX Fc (rFIXFc) in children with severe hemophilia B
Objective:
The ongoing rFIXFc extension study, B-YOND (clinicaltrials.gov #NCT01425723) , evaluates the long-term safety and efficacy of rFIXFc for the treatment of severe hemophilia B. Here we report interim safety and efficacy data for children aged <12 yrs enrolled in B- YOND.
Methods:
Upon completing Kids B-LONG, eligible subjects could enroll in one of the 3 prophylactic treatment groups in B-YOND: weekly (20 to 100 IU/kg every 7 days), individualized (100 IU/kg every 8 to 16 days, or twice monthly), or modified (a prophylaxis regimen different from weekly or individualized prophylaxis). Subjects could change treatment groups at any point in the study. The primary endpoint was development of inhibitors. Secondary outcomes included annualized bleeding rate (ABR) and rFIXFc exposure days (EDs).
Summary:
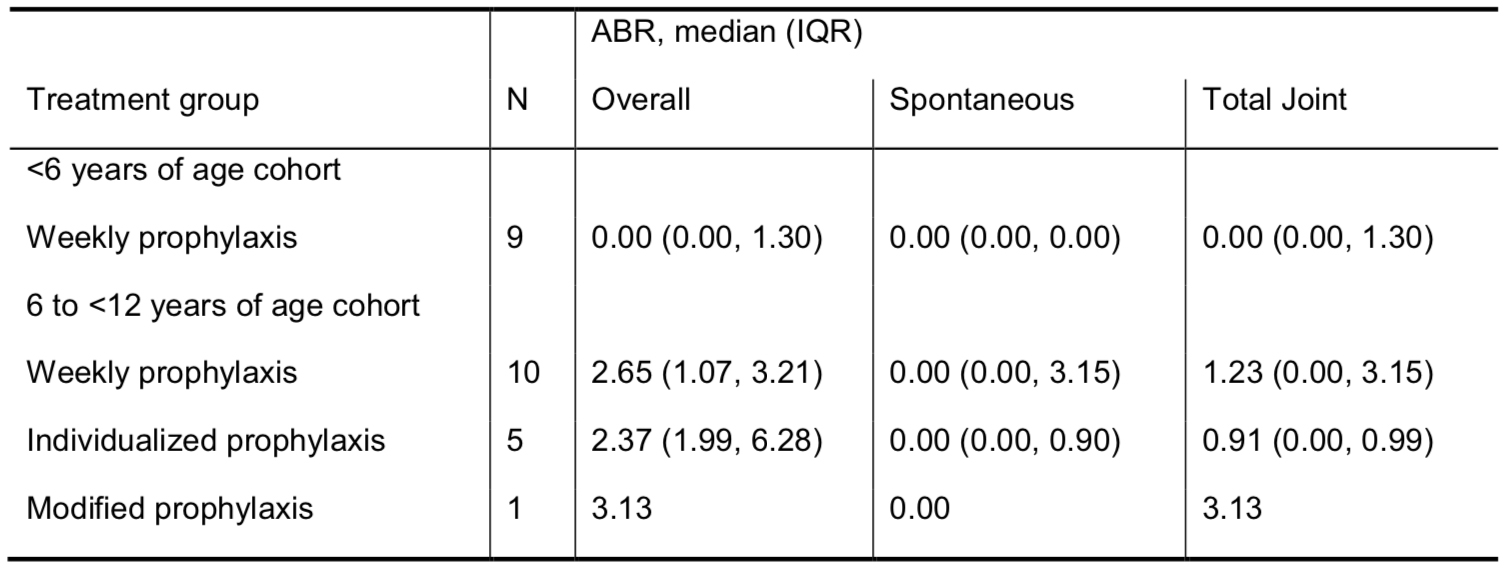
At the time of the interim data cut (17 October 2014), 23 subjects had completed Kids B-LONG; all enrolled in B-YOND (<6 yrs of age cohort, n=9; 6 to <12 yrs of age cohort, n=14). As of the interim data cut, 2 subjects had completed and 21 subjects continued in B-YOND (median time on study: 47.7 weeks). From the start of Kids B-LONG to the B-YOND interim data cut, the median time on rFIXFc was 95.3 weeks, with a median of 94 cumulative rFIXFc EDs. All subjects were on weekly prophylaxis in Kids B-LONG; 5 subjects changed treatment groups at the start of or during B-YOND. In the weekly prophylaxis group, the median (IQR) average weekly prophylactic dose was 64 (52, 66) IU/kg and 63 (59, 64) IU/kg in the <6 yrs and 6 to <12 yrs of age cohorts, respectively. The median (IQR) dosing interval among subjects on individualized prophylaxis was 10 (10, 11) days. As of the interim data cut, no inhibitors were observed, there were no reports of anaphylaxis or serious hypersensitivity reactions associated with rFIXFc, and no thrombotic events. Adverse events were typical of the pediatric hemophilia B population; no subject discontinued the study due to an adverse event. Median ABRs were low in both age cohorts (Table). Overall, 95% of bleeding episodes were controlled with 1 or 2 infusions.
Conclusions:
Interim data in children with severe hemophilia B participating in B-YOND confirm the long-term safety of rFIXFc and the maintenance of a low ABR with extended-interval prophylactic dosing.