Leaderboard Ad
AWARDED/PRESENTED: 2017
GRANT/PROGRAM:
Bleeding Disorders Conference
Orthopedic and Physical Therapy
Addressing issues of women and girls with blood disorders (WGBD) through a collaborative obstetrics/gynecology, adult and pediatric hematology lifespan clinic: a pilot project
Year: 2017
Grants:
Bleeding Disorders Conference
Collaboration/Team Models
Mild-Severe Hemophilia B Impacts Relationships for US Adults and Children With Hemophilia B and Their Families: Results From the Bridging Hemophilia B Experiences, Results, and Opportunities Into Solutions (B-HERO-S) Study
Year: 2017
Grants:
Bleeding Disorders Conference
Psychosocial Issues
Objective:
The B-HERO-S study evaluated the impact of mild-severe hemophilia B on the lives of affected adults and children. Here we assess the impact of hemophilia B on relationships.
Methods:
US adults with hemophilia B and caregivers of affected children completed separate 1-hour online surveys that included questions regarding impact on interpersonal relationships.
Summary:
Most (88%) of the 299 adults completing the survey had mild-moderate hemophilia B. Of those, 54% were married or in a long-term relationship, and 44% were single. Most adults (87%) reported that hemophilia impacted their ability to form close relationships with partners or prospective partners; 35% were very/quite dissatisfied with the support received from a previous partner. Ninety percent reported that their experiences in a prior relationship, including satisfaction with support from their previous partner, impacted their decision to enter a relationship with their current partner. Nearly all participants (98%) were very/quite satisfied with the support received from their current partner. The top reason for satisfaction was “my partner takes the lead in providing financial security” (45%). Most were very/quite satisfied with the support from family (87%) and friends (96%). Most participants reported a negative reaction or experience as a result of disclosing their hemophilia (friend/colleague/employer, 76%/80%/82%); some reported having felt bullied by peers/colleagues (69%/66%). Majorities reported that past experiences impacted which friends/colleagues they told about their hemophilia, and how or when they disclosed their hemophilia status to these individuals (97%/95%). Seventy-four percent of participants indicated that hemophilia has affected the quality of their sex life; only 54% were extremely/moderately satisfied with their overall sexual relationship. Many reported having had a bleed during sex (40%). Of 150 caregivers of children with mostly mild-moderate hemophilia (74%), 89% were married or in a long-term relationship, and most felt very/quite supported by their partner (98%) and family (87%). Impact on unaffected siblings was more often mixed (49%) than negative (18%). Most felt very/quite satisfied with support of teachers (91%), children at school (80%), and other adults in regular contact (72%). Most caregivers reported negative experiences telling a friend (76%) or having their child tell a friend (69%) about the child’s hemophilia; 43% reported that their child was bullied as a result of having hemophilia.
Conclusion:
While the impact of severe hemophilia on relationships has been reported in HERO and other studies, B-HERO-S suggests that mild-moderate hemophilia B also significantly impacts relationships of affected men/women and boys/girls, especially in terms of disclosure, intimacy, and feeling bullied by peers/colleagues. Opportunities may be explored to more proactively counsel individuals with mild-moderate hemophilia B and families in the setting of comprehensive care to better navigate interpersonal relationships and improve quality of life.

Pavan K. Bendapudi
Year:
-
Grants:
NHF-Takeda Clinical Fellowship
At the time of his application, Dr. Pavan Bendapudi was finishing his third year of adult hematology/oncology training at the combined Dana Farber Cancer Institute- Massachusetts General Hospital (DFCI-MGH) fellowship program. After finishing his medical degree at Stanford University, he did his residency in internal medicine at MGH, where he developed a strong interest in bleeding and clotting disorders. This led him to complete an additional fellowship in blood banking and transfusion medicine through the Harvard Combined Transfusion Medicine Program, where he was the first graduate of his residency program to have pursued additional training in this area.
As a hematology fellow, Dr. Bendapudi provided care to patients at the hemostasis clinic at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, and pursued additional research opportunities in the labs of Dr. Robert Flaumenhaft and Dr. Bruce Furie. Dr. Bendapudi received a Mentored Research Award from the Hemostasis and Thrombosis Research Society (HTRS) and will join the faculty at Massachusetts General Hospital as an instructor with an appointment in the Division of Hematology. While a NHF-Baxalta Clinical Fellow, Dr. Bendapudi will participate in the Comprehensive Hemophilia Clinic at Children's Hospital Boston, attending all clinical sessions and training under the mentorship of Dr. Ellis Neufeld. Dr. Bendapudi will continue expanding his training, along with a focus on the transition from pediatric to adult hemophilia care.

Angela C. Weyand
Year:
-
Grants:
NHF-Takeda Clinical Fellowship
Dr. Angela Weyand is a pediatric hematology/oncology fellow at The University of Michigan, Mott Children's Hospital. She is a native of Kansas City, Kansas and a graduate of Northwestern University in Evanston, Illinois. Dr. Weyand attended medical school at the University of Michigan and completed her pediatrics residency at the University of Washington/Seattle Children's Hospital. As a NHF-Baxalta Clinical Fellow, she will receive dedicated clinical training in the care of patients with disorders of hemostasis, as well as continuing her current research projects investigating genetic modifiers of coagulation in a zebrafish model. Dr. Weyand will be seeing patients with hemophilia and other hemostatic disorders under the mentorship of Dr. Steven Pipe and Dr. Jordan Shavit, and Dr. Pipe will include her in the management and interpretation of test results in their special coagulation laboratory. Dr. Weyand's long term goals are to further the field of coagulation through translational research and to provide the highest level of comprehensive clinical care to patients with hemophilia and coagulation disorders.
A Feasibility and Usability Study of a Nursing-Orchestrated, Customized Immersive 3 Dimensional Virtual Reality Environment in Children with Hemophilia Undergoing Routine Intravenous Procedures
Year:
-
Grants:
Nursing Excellence Fellowship
The purpose of this project is to request support for the development of a Virtual Reality Environment (VRE) study program for pediatric patients diagnosed with hemophilia. The VRE program proposed was developed and created for children and includes interactive imagery, character avatars and colorful visual environments. This VRE program will be deployed by the child in a clinical setting and is proposed to help decrease, anxiety and needle phobia during intravenous factor infusions. Outcome measures will include an anxiety scale before and after each infusion, collection of biophysiologic data, pain score and visual analogue evaluation. The expected result of this nursing project is to monitor the use of a VRE in the pediatric population with a reduction of fear, anxiety and pain experienced with intravenous factor infusions.
Molecular Basis of Procofactor to Cofactor Activation in FVIII
Year:
-
Grants:
Bob and Margaret Carton
Judith Graham Pool Postdoctoral Research Fellowship
Hemophilia A (Factor VIII/F8)
Dr. Parthasarathy's research will tackle two important biological issues in coagulation - namely how procofactor FVIII converts to the active cofactor form (FVIIIa) and binds to IX and X, and the location of FVIII in generating the active Xase complex. Results from this study will provide molecular and biochemical insights into the role of FVIIIa in regulating hemostasis and further elucidate the interactions between coagulation complexes. Dr. Parthasarathy obtained his Masters in Biotechnology from Jawaharlal Nehru University in New Delhi, India and received his Ph.D. in Biochemistry from the University of Kansas in 2011. He has been a postdoctoral researcher in the lab of Dr. Rodney Camire at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia since July 2011. This award has been made possible through a generous donation from Hemophilia of Georgia, Inc.
Mothers' Perceived Vulnerability, Protective Behaviors and Stress in Relation to Their Sons with Hemophilia
Year: 2016
Grants:
Social Work Excellence Fellowship
It is unknown if there are differences in attitudes and behaviors between mothers of sons with hemophilia who have a known family history of hemophilia compared to mothers without a known family history. To capture these differences, this study will measure mothers' perceived vulnerability of their sons, protective behaviors toward their sons and reported stress in the mother-son relationship. Sixty mothers will complete the following surveys: Parent Protection Scale, Child Vulnerability Scale and Parenting Stress Index/Short Form. The results of this data will influence clinic social work practice in the comprehensive care model at hemophilia treatment centers.

Anti-fibrinolytic Strategies to Decrease Bleeding in Hemophilic Arthropathy
Year:
-
Grants:
Career Development Award
Hemophilic Arthropathy
Pain
Dr. von Drygalski's research focuses on better understanding the mechanisms operating the anti-fibrinolytic system and how this process works in patients with hemophilia and specifically with joint bleeding. Accelerated fibrinolysis and clot instability are becoming increasingly recognized as contributing factors to bleeding in hemophilia. One important molecule that prevents fibrinolysis is called TAFI (Thrombin Activatable Fibrinolysis Inhibitor). Dr. von Drygalski will be studying the dual anti-fibrinolytic and anti-inflammatory functions of TAFI in hemophilia arthropathy and develop a therapeutic TAFI-based approach to improving the efficacy of FVIIa based bypassing strategies for acute bleeding and joint protection. Her mentors and collaborators are John H. Griffin, PhD, Laurent O. Mosnier, PhD and Martin Lotz, MD, distinguished researchers at UCSD -The Scripps Research Institute. Dr. von Drygalski received her M.D. from the Universities of Erlangen/Nurnberg and Munich in 1995 and her Pharm.D. from the University of Munich in 1988. She joined the faculty in July 2011 as Assistant Clinical Professor at UCSD and Director of the Adult Hemophilia and Thrombosis Treatment Center, Division of Hematology/Oncology, Department of Medicine. She also has an appointment as Adjunct Assistant Professor at the Scripps Research Institute (TSRI). The funding for this award is made possible thanks to a generous grant from Novo Nordisk.

Mechanoregulation of von Willebrand Factor Inhibition and Activation
Year:
-
Grants:
Rueleen Kapsch
Judith Graham Pool Postdoctoral Research Fellowship
Von Willebrand Disease
Per Dr. Fu, the JGP provided her with the opportunity to work on hemophilia, as well as von Willebrand disease. After the completion of her JGP project, Dr. Fu remained in the bleeding disorder field.
A Comprehensive and Unbiased Screen of ADAMTS13 Substrate Specificity
Year:
-
Grants:
Judith Graham Pool Postdoctoral Research Fellowship
Von Willebrand Disease
Per Dr. Kretz, the JGP award came at an ideal point in his career. Through the JGP Program, the support of the NHF plays an important role in developing young and promising research in hematology and bleeding disorders. He is truly grateful for the support of the NHF during his training and considers the award to be an important moment in his career.
The work supported by the JGP Fellowship led to two publications, one in PNAS and another in Scientific reports.

Exercise Versus DDAVP in Patients with Mild Hemophilia A - Which Is Better and Do They Work Additively in Improving Hemostasis?
Year: 2016
Grants:
Physical Therapy Excellence Fellowship
Preliminary work done by Dr. Riten Kumar and colleagues has documented that moderate intensity exercise is associated with a significant improvement in multiple coagulation parameters in post-adolescent males with mild-moderate hemophilia A. As a continuation to our previous work, we now hope to compare the impact of moderate intensity exercise to DDAVP on laboratory coagulation parameters in post-adolescent males with mild hemophilia A. We also hope to investigate the impact of sequentially administering these interventions on hemostatic indices. Our over-arching hypothesis is that increase in coagulation parameters (particularly FVIII:C) with moderate intensity aerobic exercise would be non-inferior to DDAVP. We additionally hypothesize that we will appreciate an additive effect of sequentially administering clinical implications for patients with MHA. It may negate the use of DDAVP pre- exercise and could potentially lead to clinicians advising patients to appropriately warm-up (e g running), to raise their FVIII/VWF levels prior to undertaking more rigorous sports. It will also lay the foundation for future studies investigating the interaction between aerobic exercise and hemostasis in subjects with bleeding disorders these interventions. Should our hypothesis be correct, our study would have significant clinical implications for patients with MHA. It may negate the use of DDAVP pre-exercise and could potentially lead to clinicians advising patients to appropriately warm-up to raise their FVIII/VWF levels prior to undertaking more rigorous sports. It will also lay the foundation for future studies investigating the interaction between aerobic exercise and hemostasis in subjects with bleeding disorders.

Maissaa Janbain
Year:
-
Grants:
NHF-Takeda Clinical Fellowship
Dr. Maissaa Janbain was born in Lebanon and received her M.D. degree from the Lebanese University in 1999. After completing her internship and residency in Internal Medicine in Lebanon, she came to the U.S., where she completed a second internship and residency in internal medicine at Case Western Reserve University in Ohio. She then entered the Hematology/Oncology Fellowship program at Tulane University, which she is scheduled to complete in 2015. Dr. Janbain has developed a strong interest in coagulation medicine and has spent much time receiving guidance from her mentor Dr. Cindy Leissinger, Director of the Louisiana Comprehensive Hemophilia Center. In conjunction with Dr. Leissinger, she has worked on clinical research projects for porcine rFVIII and FXIII. Dr. Janbain has not only had several research abstracts accepted but also presented at several professional meetings. She is interested in global assays and thromboelastometry. She has been applying this technique to assess FVIII and VWF in pregnant women.
The Use of High Resolution Power Doppler Musculoskeletal Ultrasound (MSKUS) in Bleeding Disorders
Year:
-
Grants:
Nursing Excellence Fellowship
The project's ultimate goal is to expand nursing knowledge of hemarthrosis/soft-tissue bleeding detection by presenting our HTC's experience with how MSKUS improves accurate diagnosis and guides treatment of bleeding and other pain etiologies. By completing the retrospective data review, we hope that the experience of a large center HTC spanning both adults and pediatrics will be made available. We believe that the current restraints of MSKUS implementation include cost of equipment, operator certification, and quality of interpretation to guide interventions. Therefore, partnering with radiology experts may be helpful for other HTCs around the country when using this modality in the future. Our center's experience will show that collaboration with radiologists for real-time imaging is successful with nursing evaluation and coordination.

Lindsey A. George
Year:
-
Grants:
NHF-Takeda Clinical Fellowship
Dr. Lindsey George is a pediatric hematology/oncology fellow at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. As a NHF-Baxalta Fellow, Dr. George will receive clinical training under the mentorship of Dr. Leslie Raffini, Director of the Hemophilia Treatment Center at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. She will also be pursuing training in translational science in coagulation molecular biology and gene transfer in the laboratory of Dr. Katherine High. Dr. George graduated from Cornell University and received her M.D. from the State University of New York at Buffalo School of Medicine. She did her pediatric residency and chief residency training at Weill Cornell Medical School, where she had the fortunate opportunity to interact with Dr. Donna DiMichele. Dr. George has a longstanding interest in the intricacies of coagulation physiology and the incorporation of that understanding to the clinical care of patients with coagulation disorders. Dr. George hopes to contribute to the improvement of treatment for patients with bleeding and thrombotic disorders through a career in translational research.

Stacy E. Croteau
Year:
-
Grants:
NHF-Takeda Clinical Fellowship
Dr. Stacy Croteau received her B.S. and M.S. in Neuroscience, and her M.D. at Brown University, where she was awarded AOA. She was resident and chief resident in pediatrics at Boston's Children's Hospital and received the Sydney Farber Award. At the time of her application, she was a third year Pediatric Hematology-Oncology fellow at Boston Children's Hospital and was accepted on faculty at Harvard as an instructor in pediatrics. Her research during fellowship was on a clinical review of Kaposi form Angioendotheliomas which resulted in 2 publications in the Journal of Pediatrics (2013, and 2014) as well as an ASH Trainee Research Award. She was the first fellow to complete the BCH-Novartis Clinical Fellowship in Early Oncology Drug Discovery. While a NHF-Baxalta Clinical Fellow, Dr. Croteau will be mentored by Dr. Ellis Neufeld, Medical Director of the Boston Hemophilia Center. She also has plans to pursue clinical research in “rationally designed personalized prophylaxis regimensâ€.

Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Platelet Therapy for Hemophilia A
Year:
-
Grants:
Judith Graham Pool Postdoctoral Research Fellowship
Platelets
Hemophilia A (Factor VIII/F8)
Dr. Noh's research will utilize induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) and manipulate them in vitro to expand production of megakaryocytes and platelets that express therapeutic proteins, including FVIII. The project will further determine whether this system of autologous platelets which overexpress FVIII can be delivered directly to the site of injury and hemorrhage, thereby circumventing and evading neutralization by alloantibody inhibitors in hemophilia A. Dr. Noh received her Ph.D. in Preventive Pharmacology from Seoul National University in South Korea. She has been a postdoctoral fellow in Dr. Mitchell Weiss' lab at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia since 2012. Dr. Noh is currently being mentored in this JGP project by Dr. Mortimer Poncz at CHOP.
Adherence influences annualized bleeding rate during prophylaxis with turoctocog alfa: results from the guardian™1 trial
Year: 2015
Grants:
Bleeding Disorders Conference
Biomedical/Coagulation Research
Hospitalization for Acute Bleeding Events among Individuals with von Willebrand Disease (VWD) in the United States
AWARDED/PRESENTED: 2015
GRANT/PROGRAM:
Bleeding Disorders Conference
Biomedical/Coagulation Research
BAY 81-8973: Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Adolescents, Adults, and Children With Severe Hemophilia A
Year: 2015
Grants:
Bleeding Disorders Conference
New Products
Introduction:
BAY 81-8973 is Bayer’s new full-length recombinant factor VIII product in development for the treatment of hemophilia A, with no human- or animal-derived raw materials added to the cell culture, purification, or formulation process. The pharmacokinetic (PK) properties of BAY 81-8973 were investigated in 3 studies in previously treated adults, adolescents, and children.
Methods:
For all PK evaluations, a single dose of 50 IU/kg BAY 81-8973 was injected. Serial blood samples were collected over 48 hours in adults and 24 hours in children <12 years of age. PK samples in adolescents and adults were analyzed using one-stage and chromogenic assays. Limited samples were collected in children and were analyzed using only the chromogenic assay. Ethnic subgroups included Chinese, Japanese, and non-Asian patients.
Results:
PK parameters using the chromogenic assay for children (aged <12 years), adolescents (aged 12–17 years), and adults (aged ≥18 years) are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Pharmacokinetic Parameters Based on the Chromogenic Assay
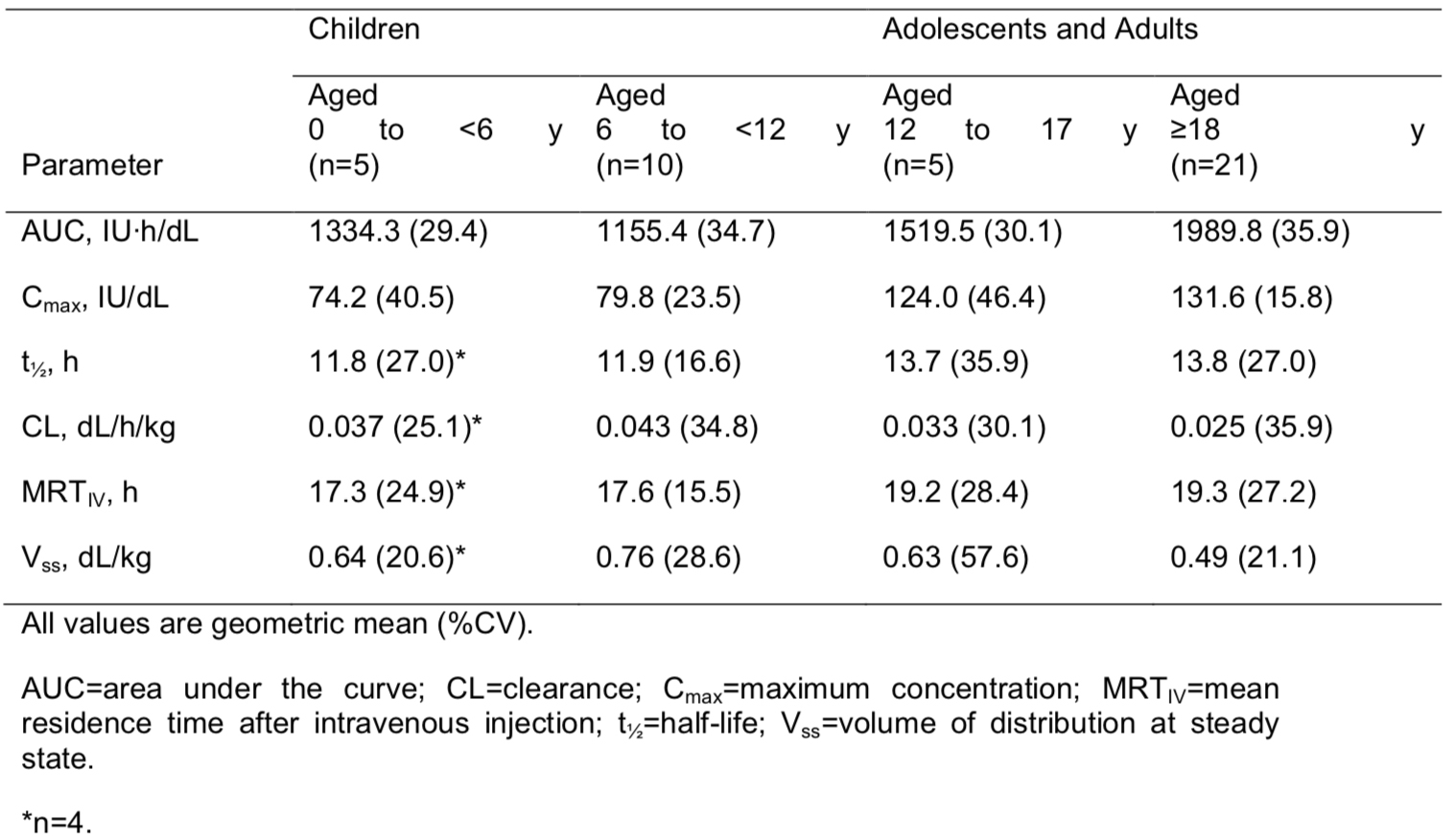
Conclusions:
Analysis of PK across the different age groups showed that the values for maximum concentration (Cmax) and area under the curve (AUC) for adolescents were within the range of those seen for adults. PK values were slightly lower in children than in adults. There were no significant differences among the ethnic groups studied.

