H. Pylori as a cause of iron deficiency in children with bleeding disorders
Objective:
Describe the role of H. pylori as a cause of chronic iron deficiency in children with congenital bleeding disorders.
Methods:
As part of their routine comprehensive care children at our haemophilia treatment center have a CBC done. Over the past year 4 children who underwent diagnostic workup for microcytic anemia were found to have iron deficiency associated with H. pylori infection. We describe the clinical findings in these children and their outcomes after appropriate therapy.
Summary:
From March 2012 to March 2013, 4 children were identified with iron deficiency anemia due to H. pylori. None of the 4 patients gave a history of excessive blood loss and none had GI symptoms such as weight loss, abdominal pain, vomiting or diarrhea. Clinical and laboratory findings at presentation are summarized below. No patients had thrombocytopenia.
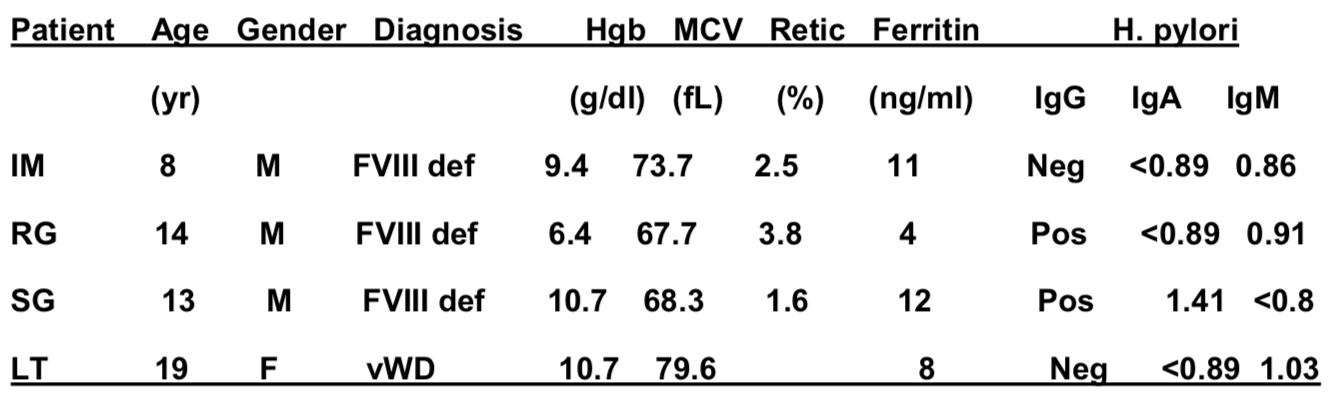
Only one patient had positive occult blood in stool (RG) and underwent endoscopy. Diagnosis of H. pylori was made on gastric biopsy. RG also had 4 weeks of IV iron sucrose therapy. All patients were seen by gastroenterology and successfully treated with triple therapy consisting of amoxicillin, Biaxin, and omeprazole. RG had a recurrence and was retreated with quadruple therapy consisting of amoxicillin, metronidazole, omeprazole, and bismuth subsalicylate. All 3 patients with FVIII deficiency were also on secondary prohylaxis.
Conclusions:
H. pylori is a common cause of gastritis and often presents with upper gastrointestinal symptoms. It is also associated with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. However, in children with congenital bleeding disorders, it may present with few symptoms and an incidental finding of iron deficiency anemia. We suggest that children with bleeding disorders should be screened for H. pylori as a cause of iron deficiency.


