Utilization of Telehealth for Home Infusion Teaching and Support in the COVID Era
Characterization and management of patients with mild or moderate hereditary factor X deficiency: a retrospective chart review
The World Federation of Hemophilia World Bleeding Disorders Registry: A Two-year Update
The Impact of Novel Hemophilia Treatment Products on Inhibitor Testing for the Community Counts Registry for Bleeding Disorders Surveillance
Optimizing language to increase understanding, improve communication, and manage expectations around gene therapy for hemophilia: a qualitative study
Development of the WFH-ISTH Gene Therapy Registry
Continuous infusion of B domain-truncated recombinant factor VIII, turoctocog alfa, for an acute moderate bleeding episode in hemophilia A: a first case report
A Review of Current Patient Reported Outcome Measures Used to Assess Mental Health in People with Hemophilia
A Novel Approach for Rare Bleeding Disorders: Shielded Living Therapeutics
The 2020 World Federation of Hemophilia Guidelines for the Management of Hemophilia
Behavior and cognition in children and young adults with hemophilia A or B: an update on developmental outcome
Characterization of the Early Immune Response to Factor VIII
Unmet Needs in Women with Severe Von Willebrand Disease
The Moti-VIII Study – Factors for Empowering Mobility and Well-being in Hemophilia A
Retrospective review of Hemophilia patients before and after treatment with Emicizumab
Assessing and Responding to the Oral Health Care Needs of Adults in a Bleeding Disorders Population
Introduction/Background:
Maintenance of oral health is frequently challenging for US adults with a bleeding disorder. Underlying causes are due mainly to (1) lack of dental insurance and (2) lack of knowledge among dentists about how to perform safely either primary dental care or oral surgery. Without regular care, patients are at risk for advanced dental disease, which is associated with chronic inflammatory conditions, including type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Research indicates that controlling periodontal disease reduces inflammatory markers throughout the body, including synovial joints.
Materials and Methods:
The Gulf States Hemophilia and Thrombophilia Center (GSHTC) in Houston, Texas serves a diverse urban population; historically, about 50% of adult patients receive no dental care. In October 2019, GSHTC added adult dental exams to comprehensive care services. Patients are evaluated by University of Texas School of Dentistry residents and scheduled for routine or specialized dental procedures as needed. To assess the scope of dental needs in the GSHTC patient population, we examined the range of procedures recommended and the proportion of patients reporting oral health care problems. We report here preliminary results from the initial six months of adult dental services, October 2019 – March 2020.
Results:
In this period, 171 adults with a bleeding disorder received dental evaluations, and 146 completed the Oral Health Impact Profile (OHIP-14). The OHIP-14 is a validated survey instrument consisting of 14 questions measuring seven dimensions of oral health: functional limitation, physical pain, psychological discomfort, physical disability, psychological disability, social disability and handicap. Responses are rated on a 5-point Likert scale: 0=never, 1=hardly ever; 2=occasionally, 3=fairly often; 4=very often/every day. Total OHIP-14 scores can range from 0 to 56 and are calculated by summing the values for the 14 items. Higher scores indicate worse and lower scores indicate better health-related quality of life (HRQoL). Scores ranges from 0-52; 80 (55%) individuals had a score of 0-1 (no oral health problems); 48 (33%) scored between 2-9, and 18 (12%) had scores of 10 or greater. Since October 2019, nearly all adult patients seen in clinic have received a dental evaluation; approximately 40 patients in need of dental care have received treatment or a treatment plan. Procedures include deep cleaning, regular/surgical extractions, fillings, scaling, root planing, crowns, bridges and root canal, all of which require infusion of factor concentrate prior to treatment.
Conclusion:
A substantial proportion of patients who completed the OHIP-14 reported reduced HRQoL related to poor oral health; subsequent dental examination confirmed the urgent need for treatment in these individuals. Continued administration of the OHIP-14 will monitor the impact of dental treatment on patient HRQoL. Ultimately, we hope to provide evidence of the need for widespread inclusion of adult dental care among US Hemophilia Treatment Centers.
Redefining Treatment Satisfaction and Its Impact on Treatment Adherence and Value for Persons with Hemophilia: Findings from the HemACTIVE Study
Bone and joint health markers in persons with hemophilia A treated with emicizumab in the HAVEN 3 clinical trial
Objective:
Multiple factors contribute to bone health, including physical activity, lifestyle, diet, and certain medical conditions. Emicizumab prophylaxis has been shown to reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes in persons with hemophilia A (PwHA). In this study, we explored the potential effect of emicizumab prophylaxis on joint health scores and biomarkers of bone health in PwHA without factor VIII (FVIII) inhibitors who participated in the HAVEN 3 clinical trial.
Methods:
The Hemophilia Joint Health Score (HJHS) is a tool used to assess joint function and gait, with a lower score indicating better joint health. We obtained HJHS scores from 107 PwHA before starting emicizumab and 48 weeks after starting emicizumab. We also measured biomarkers for bone and joint health in blood samples from 117 PwHA; blood samples were taken before starting emicizumab, and periodically after starting emicizumab (3, 6, 12, and 18 months). In total, 78 people received both the HJHS evaluations and biomarker testing.
Summary:
PwHA who were previously on FVIII prophylaxis and those with no target joints had lower HJHS (indicating better joint health) before starting emicizumab. Average HJHS values decreased 48 weeks after starting emicizumab, indicating improvement in joint function and health. There were 71 people with at least one target joint; among those we saw improvements from baseline in the average total HJHS (-2.25 [95% confidence interval: -4.12, -0.39]) and significant improvements in the joint-specific part of the HJHS, which excluded gait (-2.23 [95% confidence interval:-4.07, -0.38]). Improvement was consistent across HJHS for different joints. Before starting emicizumab, there were no significant differences in biomarkers for bone health between PwHA previously on FVIII prophylaxis or on on-demand treatment, or those with or without target joints. The average values measured for most of the markers were within normal ranges, or were similar to values for healthy individuals documented in the scientific literature; although there was a large variation among individuals tested. None of the measured biomarkers changed significantly during emicizumab prophylaxis. Among the adolescents in this study, levels for three of the biomarkers known to increase during periods of growth were higher than in the adults at each time point.
Conclusions:
This analysis showed clinically relevant improvements in HJHS (defined as a ≥2-point decrease in the joint-specific part of the HJHS) 48 weeks after starting emicizumab prophylaxis in PwHA without FVIII inhibitors. Average values for most of the biomarkers for bone and joint health were similar to values reported in healthy people without hemophilia A, and did not show significant changes during emicizumab prophylaxis. We saw no indication of worsening of the markers for bone and joint health. Additional data are needed to better understand the long-term effect of prophylaxis on bone and joint health.
Summary of thrombotic or thrombotic microangiopathy events in persons with hemophilia A taking emicizumab
Non-severe hemophilia is not benign? - Insights from the PROBE Study
3 apps in 1: MyCBDR, myWAPPS and myPROBE
A systematic review of mortality statistics and causes of death in people with congenital hemophilia A (PwcHA)
Characteristics of persons with hemophilia A treated with emicizumab with or without factor VIII inhibitors
Final Results of PUPs B-LONG Study: Evaluating Safety and Efficacy of rFIXFc in Previously Untreated Patients With Hemophilia B
Final Results of PUPs A-LONG Study: Evaluating Safety and Efficacy of rFVIIIFc in Previously Untreated Patients With Hemophilia A
Evaluating BIVV001, a New Class of Factor VIII Replacement Therapy: A Phase 3 Study (XTEND-1) Design
The Need for Comprehensive Care for Persons with Chronic Platelet Disorders
Treatments and Clinical Outcomes of Bleeding Related to Pregnancy, Surgery, or Spontaneous or Traumatic Bleeds in Women and Girls With Factor VIII and IX Deficiency: Results From a Retrospective Chart Review
An analysis of fatalities in persons with congenital hemophilia A (PwcHA) reported in the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database
A contemporary framework for understanding mortality in people with congenital hemophilia A (PwcHA)
A single administration of AAV5-hFIX in newborn, juvenile and adult mice leads to stable hFIX expression up to 18 months after dosing
Progress Update on the Development of Etranacogene Dezaparvovec (AMT-061) in Severe or Moderately Severe Hemophilia B
Vector DNA clearance from bodily fluids in patients with severe or moderate-severe hemophilia B following systemic administration of AAV5-hFIX and AAV5-hFIX Padua
An ECHO’d Practice: Utilizing Tele-Mentoring for Enhanced Data Quality Across One Hemophilia Treatment Center Region
Real-world treatment patterns, health outcomes, and healthcare resource use among persons with hemophilia A
Case Report of Surgical Management of a Hemophilia B Gene Transfer Clinical Trial Participant Following Etranacogene Dezaparvovec (AMT-061) Gene Therapy
Supporting patient voice to inform healthcare decision-making: a discrete choice experiment on disability paradox in hemophilia
Analysis of Bleeding and Treatment Patterns in Children and Adolescents before and after Von Willebrand Disease Diagnosis Using Data from a US Medical Claims Database
Adding the patient's voice to a hemophilia-specific goal menu to facilitate Goal Attainment Scaling: a qualitative study
Incidence and Prevalence of Diagnosed and Undiagnosed Hemophilia A and Hemophilia B in the USA
Overview of the clinical development of fitusiran
Intra-individual across-study comparison of the pharmacokinetics of rFVIII-FS, BAY 81-8973 and BAY 94-9027 in patients with severe hemophilia A
A US payer database algorithm to identify clinical profiles of hemophilia B for burden of illness assessment
On My Own, A Pilot Transition Program for Teens
Objective:
To educate teens and their siblings on building skills related to self-care, medical independence and living a healthy lifestyle so that they are better prepared to be on their own as they transition to the next stage in life: adulthood.
Methods:
A collaborative, multidisciplinary team consisting of team members from the Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center Hemophilia Treatment Center (HTC) and the Tri-State Bleeding Disorder Foundation lead 14 teens attending a family bleeding disorder educational conference in an interactive, educational program.
Participants were teens (ages 12-17) with a bleeding disorder and their siblings. Participants worked in teams and visited six different booths where they engaged in interactive activities such as role playing, exercising and games. Booths were staffed by the HTC staff that included nurse care managers, pharmacists, data manager, social worker, health educator, and a physical therapist. Each booth focused on: genetics of a bleeding disorder, digital citizenship, managing home treatment independently, understanding bleeding disorders, insurance/career planning and fitness /healthy joints.
This evidenced-based educational content was based on the Medical and Scientific Advisory Council (MASAC) transition guidelines for people with a bleeding disorder (Belling e al., 2003). The content and program design was also rooted in the social cognitive theory with elements of vicarious learning, behavioral capability, and self-control.
Summary:
An interactive and evidenced-based teen transition program allowed for teens to gain knowledge in various topics related to gaining in medical independence and self-care skills. All teens that participated in the program demonstrated an increase in knowledge at the program’s end.
Conclusions:
All participants showed an increase in scores from pre-test to post-test. The average scores increased by 20%. The team plans to implement this program again in the future.
References:
Belling L., Harrop M., Kocik S., Obstein, L., Standish, D., Vlasich, W., & Zappa, S. (2003). Transition Guidelines for People with Bleeding Disorders. New York, NY: M.A.S.A.C, 147, 1.
Longitudinal trends of patient-focused programs in the bleeding disorders community from 2013-20: a retrospective analysis of Hemophilia Alliance Foundation grants
Fear of pain in people with hemophilia and their families – a pilot study
Application of attention destruction techniques during factor concentrates infusion to children with Hemophilia
Empowering the Future of Hemophilia Through Swimming (Poster Abstract)
Women and girls with hemophilia: Gender-based differences in comprehensive care
von Willebrand Factor in Pregnancy (VIP) Study: A Multicenter Study of Wilate Use in von Willebrand Disease for Childbirth
A retrospective chart review to assess clinical characteristics of women and girls with factor VIII and IX deficiency
Female Patients with Hemophilia A: A Claims-Linked Chart Review
Von Willebrand Disease: An international Survey to Inform Priorities for New Guidelines
The Patient Reported Outcomes Burdens and Experiences (PROBE) Study Questionnaire Development and Validation
Combining Data from Hemophilia Registries with the World Bleeding Disorders Registry: A Proof of Concept Study with the Czech National Haemophilia Programme Registry
Data is the new currency: The World Bleeding Disorders Registry Data Quality Accreditation Program
World Federation of Hemophilia Annual Global Survey 2017 – 19 years of reporting
World Federation of Hemophilia Annual Global Survey analysis of age distribution of patients with hemophilia
The WFH World Bleeding Disorders Registry – 16-month update
Patient Perspectives on the Impact of Severe or Moderate Hemophilia on Physical Activity: HemACTIVE Survey Findings from the US and Canada
Evaluation of Patient and Physician Reported Reasons for Switching FVIII Replacement Therapies Among Patients With Hemophilia A
Objective:
While a new generation of therapies for patients with Hemophilia A are available, it is unclear what patient characteristics, perceptions, and barriers are associated with the decision to switch FVIII replacement therapies. This study assessed patient characteristics, health history, and reasons for switching from a FVIII product with more frequent dosing (³3x infusions/week) to a product with less frequent dosing (≤2x infusions/week) from patient/caregiver and physician perspectives.
Methods:
Data collection was a mix of qualitative and quantitative procedures. The qualitative portion consisted of two online discussion forums: patients (n=17) and caregivers of patients (n=11) receiving a FVIII product dosed ³3x/week, and patients (n=22) and caregivers of patients (n=5) who switched to a product dosed ≤2x/week. The quantitative portion was a retrospective medical chart review (n=207) which captured variables (e.g., bleed rate, treatment history) 6 months pre- and 6 months post-switching to a product with less frequent dosing.
Summary:
Prominent drivers among patients for starting a FVIII product with less frequent dosing included: 1) experiencing diminished effectiveness while on a product dosed ³3x/week resulting in increased breakthrough bleeding, 2) experiencing vein access issues, and 3) beginning prophylaxis as opposed to on-demand infusions after a bleed.
Key barriers to changing included: 1) fears regarding the process of switching being complicated, time consuming, and costly, 2) perceived risks associated with switching, and, 3) possible lack of healthcare provider support.
Physicians were most likely to report that patients switched products because they sought a newer product with twice weekly dosing or less per FDA-approved dosing recommendations (35.3%), followed by patient requested the switch (30.4%), and patient sought a reduction in infusion frequency to improve adherence (27.5%).
Switching to a product with less frequent dosing was associated with improvements in patient-reported bleeding-related outcomes. Patients were more likely to self-administer the treatment post-switch (63.8%) compared with pre-switch (48.8%; p<0.001) and had fewer infusions per week post-switch (2.8 vs. 3.3; p<0.001). Patients’ annualized bleed rate was lower (5.9) post-switch compared with pre-switch (7.7; p<0.001).
Both the number of spontaneous joint bleeds and joint bleeds after trauma or injury were lower (3.2 and 2.7) post-switch (3.6 and 4.3; p=0.044 and p<0.001). The bleeding event was less likely to be classified as moderate or severe (34.5% and 5.9%) post-switch compared with pre-switch (55.0% and 10.0%; p<0.001 and p=0.049). Fewer infusions were required to resolve the bleeding event post-switch (2.6 vs. 3.2; p<0.001).
A prominent reason why patients switch treatment is to improve bleeding-related outcomes. Indeed, we found that switching to a FVIII product with less frequent dosing was associated with improved patient-reported bleeding-related outcomes. These findings are critical for improving patient outcomes and support the FDA mandate to incorporate patient perspectives in the regulatory process.
Increasing Medical Alert Devices (MAD) Compliance in School Age Children with Hemophilia: A Quality Improvement Project
Patients Report High Satisfaction with US Hemophilia Treatment Centers: National Trends 2014 and 2017
Satisfaction with Teen Transition Services at US Hemophilia Treatment Centers by Center – Variation by Pediatric and Lifespan Centers 2014 and 2017
An evaluation of health utility and quality-of-life in hemophilia: a systematic literature review
Quality of life and health in patients with Haemophilia in Mexico
A look from within: a needs assessment of educational support for the Rare Bleeding Disorders Community
Objective:
The National Hemophilia Foundation Education team partnered with an evaluator to conduct a needs assessment of the rare bleeding disorder (RBD) community to help inform the development of programming tailored to the community’s unique experiences and needs.
Methods:
A guided discussion with the attendees of a Bleeding Disorder Conference (BDC) session titled, “The Lonely Island: Dealing with Being Rare” in 2018 as well as brief surveys at the end of the session were compiled as part of the needs assessment. Additionally, 12 one on one interviews of those part of the RBD community (either affected themselves or a close relative to someone that is affected) were conducted.
Summary:
Various challenges for this population were identified, including: connecting with others who have the same RBD; healthcare providers’ lack of knowledge/understanding of specific RBDs; accessing knowledgeable hematologists and RBD experts; accessing the latest science specific to their RBD; scarcity of treatment resources; difficulty getting diagnosed. Other secondary challenges were also expressed. While challenges were identified, those that participated in the needs assessment also highlighted the ways in which they see the RBD community can best be served. Common suggestions included: the addition of RBD-specific programming at NHF’s Bleeding Disorder Conference (BDC); continuing to make NHF and Chapters inclusive; creating more opportunities for the RBD community to connect with others with the same RBD (at NHF’s BDC and other events); creating targeted educational materials and opportunities for the RBD community; creating opportunities for members of the RBD community to identify and engage with the medical community.
Conclusions:
By conducting this needs assessment, NHF took an important step in asking the RBD community directly how they can best be supported given their unique experiences and needs. While challenges for the RBD community were identified, several opportunities to support the RBD community were also identified.
Identification of Orthopedic and Genetic Needs Reported by Persons with Type 3/Severe Von Willebrand Disease
Optimizing language for effective communication of gene therapy concepts: A qualitative study
The Effect of Bleeding Disorder Characteristics on Patient Perceived Challenges and Management Strategies
Objective:
To investigate how bleeding disorder characteristics influence patient perceived challenges and management strategies.
Methods:
This is a mixed-method, retrospective, cross-sectional continuation of a pilot study identifying themes of self-perceived challenges and management strategies for persons with bleeding disorders. Sixty-one participants with a bleeding disorder (BD), either hemophilia (PWH) or Von Willebrand disease (PWVWD), were asked what their most significant challenge was in managing their BD and how they managed that challenge. Data were collected from March, 2017 through December, 2018, coded for themes and uploaded to NVivo. Similar themes were grouped for analysis. Subject-level data was extracted from the electronic medical record including demographics, disease type, severity and presence of joint disease (JD). Pain interference was determined from participant response to the Brief Pain Inventory (BPI).
Results:
- The mean age of the cohort was 31.4 years, with a median of 25 years, and range of 7 to 75 years. 87% were PWH, 13% PWvWD.
- There were 26% mild, 25% moderate, and 49% severe PWH.
- 54% had JD.
- Identified challenges included: participation restriction (24%), acute bleeding (22%), infusion (19%), bleeding sequelae (10%), other’s unfamiliarity with bleeding disorder (other’s unfamiliarity) (10%), no challenges (10%), and other (6%). Management strategies reported were: acceptance (37%), learning through experience (25%), education/advocacy (11%), seeking help (9%), other (9%), and no challenges (9%).
- Severe PWH greatest reported challenges were participation restriction (27%) and infusion (27%). Management strategies were acceptance (41%) and experiential learning (31%).
- Mild-moderate PWH greatest reported challenges were acute bleeding (35%), infusion and no challenge (17% each). Management strategies were acceptance (30%) and seeks help (26%).
- Seek help was not identified as a strategy among severe PWH.
- Reports of no challenges was higher among those <18 years than those ≥ 18 years.
- Mean pain interference was 13.2 out of 70 based on the composite score of BPI measures.
- As age increased, the likelihood of JD and interference increased.
- Regardless of challenge, people with JD reported interference averaging 18% (range 0-27%).
Conclusions:
Gaining insight to patient-perceived challenges and management strategies is important to be able to tailor an effective treatment approach that is individualized and meets the changing needs of PWBD across circumstance and life-course.
Using Photovoice with the Bleeding Disorder Population: A Pilot Project
Quality Improvement: An Initiative to Foster Mental Health Wellness among a Hemophilia Treatment Center Patient Population
The impact of face-to-face social work meetings in bleeding disorder care
HemoFOCUS Screener for Inattention, Hyperactivity and Impulsivity: A Quality Improvement Intervention for Children with Severe Hemophilia
Pain assessment and treatment in bleeding disorder care: The need for social work specific education
Gender Differences in Parenting Stress and Social Support Among Hemophilia Families
Parents Empowering Parents (PEP) Community Survey: How does the community want to stay engaged, communicate, and receive information?
Behavioral Health and Substance Use Screening Practices among Hemophilia Treatment Centers
Depression in hemophilia and von Willebrand using the Beck Depression Inventory
Evaluation of Joint Bleeds Using Portable Ultrasound and Its Impact on Treatment of Persons With Hemophilia in a Resource Limited Setting
Physical Therapy and Extensions for Community Healthcare Outcomes (ECHO): Western States Hemophilia Regional Project
Use of Return to Sport Testing for Prevention of Bleeding Episodes Following an Acute Injury in the Hemophilia Patient
Tackling a New Era of Treatment in Hemophilia A: One Institution's Experience of Integrating Emicizumab into Practice
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in a Pediatric Patient with Hemophilia B: A Rare Clinical Challenge
NHF’s State Advocacy and the Bleeding Disorders Community
Validation of a FVIII Chromogenic Nijmegen Bethesda Assay for the Detection of Inhibitors in the Presence of Emicizumab (ACE-910)
Short-term efficacy of recombinant porcine factor VIII in patients with acquired factor VIII inhibitors
A Retrospective Study Evaluating Immune Tolerance Induction (ITI) with a Plasma-derived Factor VIII for Patients with Hemophilia A and High Titer Inhibitor
rFVIIIFc for first-time immune tolerance induction therapy: interim results from the global, prospective verITI-8 study
A survey among patients with hemophilia and inhibitors seeking treatment in non-hemophilia treatment centers
A multidisciplinary approach to the successful transition of a complex patient with severe hemophilia A with inhibitor to Emicizumab (Hemlibra®): A Case Study
Objective:
Demonstrate the success of collaborative efforts between the specialized multidisciplinary Infusion Pharmacy Provider (IPP), the prescriber, patient and payer, in achieving improved outcomes.
Methods:
A Case Study including chart review, cost analysis, and interviews with patient and prescriber.
Summary:
Patient is a 23-year-old male with severe hemophilia A and an inhibitor, followed by a Hemophilia Treatment Center (HTC). Patient developed a high titer inhibitor with a Bethesda Titre of 1000 BU/ml as a child. Several complex treatment plans including: Immune Tolerance Therapy (ITT) utilizing plasma derived and recombinant factor products, immunosuppressive therapy, and prophylaxis with bypassing agents failed. Complications with implanted ports resulted in hospitalizations and replacement of approximately twenty ports. Numerous hospitalizations for uncontrolled bleeding episodes and pain management contributed to a disruptive childhood/adolescence and suboptimal quality of life for the patient and family.
Patient was unable to attend school regularly, develop socially, or participate in normal age-appropriate activities. Repeated uncontrollable bleeding episodes led to the development of target joints and hemarthrosis. The complex nature of the patient’s treatment regimen, his psychosocial issues, bleed history, and cost of therapy resulted in frequent communication and collaboration between all stakeholders to maximize therapy outcomes.
Inhibitors presents a significant management challenge.2 Emicizumab (Hemlibra®) was approved for the treatment of hemophilia A with inhibitors in November 2017. Well in advance of the transition, the IPP and prescriber discussed the benefits with the patient. Although understandably reluctant due to his history of failed therapies, the patient agreed to try Emicizumab. Initial doses were administered at the IPP’s Alternate Infusion Suite (AIS) under clinical observation, per prescriber’s request. The patient and caregiver received extensive education regarding potential adverse events, self- administration, and bleed treatment regimen during these visits.
Conclusion:
The coordination of care, communication, and goal alignment by all stakeholders resulted in positive outcomes for this patient. Following eighteen months of therapy with Emicizumab, the patient reports improved over-all quality of life as evidenced by his ability to maintain employment, attend college, and engage in social events/ activities. Twenty-two hospitalizations in the twelve months prior to changing therapies decreased to one in the eighteen months after transitioning. His bleeding events decreased from six to eight bleeds per month to one bleed in the past eighteen months and this bleed was attributed to a missed dose. Education on the importance of adhering to prescribed dosing schedule was reinforced by both the IPP and HTC. His port has been removed. Along with his significant increase in quality of life, the dramatic decrease in overall cost of care will be highlighted.
Navigating the Emergency Department: A Collaboration Among Hemophilia Treatment Center Staff, Emergency Department Staff & Bleeding Disorder Chapter Staff
The Positive Impact of CME on Healthcare Providers’ Knowledge of Gene Therapy Studies in Hemophilia
Online CME as a Tool to Increase Clinicians’ Knowledge of Clinical Trial Data for Gene Therapy in Hemophilia
Four-year safety and efficacy of N8-GP (ESPEROCT®) in previously treated adolescents/adults with hemophilia A in the completed pathfinder 2 trial
Five-year safety and efficacy of N9-GP (REBINYN®) in previously treated children with hemophilia B in the ongoing paradigm 5 trial
Modeling of Daily Administration of N8-GP (ESPEROCT®) vs Standard Half-life FVIII for Patients With Hemophilia A Participating in Sports Activities
Five-year safety and efficacy of N8-GP (ESPEROCT®) in previously treated children with hemophilia A in the completed pathfinder 5 trial
Factor VIII deficiency is associated with abnormal brain volumes
Three-year efficacy and safety results from a phase 1/2 clinical study of AAV5-hFVIII-SQ gene therapy (valoctocogene roxaparvovec) for severe hemophilia A (BMN 270-201 study)
Baseline patient characteristics in ReITIrate: A prospective study of rescue ITI with recombinant factor VIII Fc fusion protein (rFVIIIFc) in patients who have failed previous ITI attempts
Objective:
Inhibitor development is the most serious complication of hemophilia A therapy. Immune tolerance induction (ITI) is the gold standard for inhibitor eradication, restoring factor VIII (FVIII) responsiveness. Retrospective data on ITI therapy using rFVIIIFc have been reported (Carcao et al. Haemophilia. 2018). The ReITIrate study (NCT03103542) was designed to prospectively evaluate success of rescue ITI with rFVIIIFc.
Methods:
ReITIrate, a prospective, interventional, multicenter, open-label study, enrolled patients with severe hemophilia A and inhibitors, who failed previous ITI attempts. The primary purpose is to describe the outcome of ITI performed with rFVIIIFc (200 IU/kg/day) within a maximum of 60 weeks. Here, patient baseline characteristics are reported using descriptive statistics and listings.
Summary:
Sixteen subjects were included in the study between November 2017 and December 2018. The median (range) age at study enrollment was 7.5 (2–46) years. Seven subjects had a known family history of inhibitors. The median (range) number of prior ITI attempts was 1 (1–3) and the median (range) total ITI duration was 51.5 (12–155) months. All subjects had previously received high-dose ITI, with 3 subjects receiving plasma products, 6 subjects receiving recombinant products, and 7 subjects receiving both recombinant and plasma products for previous courses of ITI. Four subjects received prior immunomodulatory therapy. The median (range) inhibitor titer at screening and historical peak were 11 (0.9–635) BU/mL and 127 (8–3000) BU/mL, respectively. During the 12 months prior to enrollment, the median (range) number of bleeds was 5 (0–24); 11 subjects used activated prothrombin complex concentrate (aPCC) for treatment of bleeds, 5 subjects received recombinant factor VIIa (rFVIIa), and 1 subject each received FVIII/von Willebrand factor, recombinant FVIII, and tranexamic acid. Twelve subjects received prophylaxis with bypassing agents during this period (10 aPCC, 1 rFVIIa, and 1 both products).
Conclusions:
This is the first prospective study describing rescue ITI with an extended half-life recombinant FVIII product. Enrolled subjects had multiple risk factors for poor ITI outcomes and a long duration of previous ITI. There is an unmet need for successful tolerization in such patients, allowing regular FVIII prophylaxis and potentially leading to improved clinical outcomes and quality of life.
Clinical Study to Investigate the Efficacy and Safety of Wilate During Prophylaxis in Previously Treated Patients With Von Willebrand Disease (VWD)
Objectives:
This study has a primary objective to determine the efficacy of VWF/FVIIII concentrate (Wilate) in the prophylactic treatment of previously treated patients with type 3, type 2 (except 2N), or severe type 1 VWD.
Secondary objectives of this study will be to collect data to 1) Assess the VWF:Ac and VWF:Ag incremental IVR of VWF/FVIIII concentrate over time, 2) Assess the safety and tolerability of VWF/FVIIII concentrate in this indication.
Also the study will examine, the efficacy of VWF/FVIIII concentrate in the treatment of breakthrough bleeding episodes (BEs), and in surgical prophylaxis, as well as the quality of life (QoL) during prophylaxis with VWF/FVIIII concentrate.
Methods:
The study is planned to enrol 28 PTPs aged ≥6 years and with VWD type 1, 2A, 2B, 2M, or 3. Eligible patients must be receiving on-demand treatment with a VWF-containing product, with at least 1, and an average of ≥2, documented spontaneous BEs per month in the preceding 6 months requiring treatment with a VWF-containing product. This will be assessed as part of a run in observational study to collect bleeding rate prior to the start of prophylaxis.
From the beginning of the study, patients will receive prophylactic treatment with VWF/FVIIII concentrate for 12 months and record all BEs in a patient diary. Based on these data, the frequency of BEs and the annualized bleeding rate (ABR) under prophylactic treatment will be calculated.
Treatment efficacy of BEs will be assessed by the patient (together with the investigator in case of on-site treatment) using a 4-point scale (excellent, good, moderate, none)
In case patients undergo surgeries, efficacy of VWF/FVIIII concentrate will be assessed at the end of surgery by the surgeon and at the end of the postoperative period by the haematologist. In both cases, predefined assessment criteria will be used. In addition, an overall assessment of efficacy will be made at the end of the postoperative period by the investigator.
Summary/conclusions:
Prophylactic treatment in other congenital bleeding disorders is widely accepted as the standard of care to prevent bleeding and preserve quality of life in patients. This form of treatment in VWD is not well characterized prospectively as yet. This study will provide data on the efficacy of prophylactic treatment in reducing the rate of bleeding and on the impact of prophylaxis on the quality of life in VWD patients.
Clinical experience with BIVV001, the first investigational factor VIII (FVIII) therapy to break through the von Willebrand factor (VWF) ceiling in hemophilia A
AMT-061 (AAV5-Padua hFIX variant) an Enhanced Vector for Gene Transfer in Adults with Severe or Moderate-Severe Hemophilia B: Follow-up up to 9 Months in a Phase 2b trial
No evidence of germline transmission of vector DNA following intravenous administration of AAV5-hFIX to male mice
Bleeding types and treatments in patients with von Willebrand disease before and after diagnosis
Correcting Bleeding Disorders Using Blood Clotting Factors Produced in vivo by Encapsulated Engineered Allogeneic Human Cells
Optimizing signal strength and suppressive potential of FVIII specific CAR Tregs for tolerance induction in a murine model of hemophilia A
A Unique Combination of Severe Congenital Factor XIII Deficiency and Type 2M Von Willebrand Disease – A Case Report
Surveying Nurses’ Knowledge and Confidence of Discussing Oral Health with Patients with Bleeding Disorders
PiggyBac mediated gene transfer for prevention of anti-factor VIII antibodies in hemophilia A
Impact of hemophilia on employment - Insights from the PROBE Study
Congenital afibrinogenemia: a case report of perioperative hematological management during difficult orthopedic surgery
Head-to-head pharmacokinetic comparisons of N9-GP with standard FIX and rFIXFc in patients with hemophilia B
Objective:
Nonacog beta pegol (N9-GP) and recombinant factor IX-Fc fusion protein (rFIXFc) are two modified rFIX compounds with extended half-lives compared with standard FIX products. We report results from two head-to-head, single-dose pharmacokinetic (PK) trials comparing N9-GP with standard FIX and rFIXFc in previously-treated patients (PTPs) with congenital hemophilia B (≤2% FIX).
Methods:
paradigm™1 (NCT00956345) was a first human-dose trial in PTPs investigating the safety and PK of a single N9-GP dose. Sixteen PTPs (21-55 years) received one dose of their previous FIX product, followed by one dose of N9-GP at the same dose level (25, 50, or 100 IU/kg) with ≥7 days between doses. FIX activity was assessed up to 48 hours (standard FIX) or 168 hours (N9-GP) with additional samples at 2 and 4 weeks analyzed by one-stage clotting assay (TriniCLOT™) with product-specific standard as calibrator. paradigm™7 (NCT00956345) was a multicenter, randomized, head-to-head trial where 15 patients (21-65 years) received single injections (50 IU/kg) of N9-GP and rFIXFc with ≥21 days between doses. FIX activity was assessed for up to 240 hours using a one-stage clotting assay (SynthAFax or Actin FSL) and a chromogenic assay (ROX factor IX) with normal human plasma as calibrator. The primary endpoint was area under the FIX activity–time curve from 0 to infinity, dose normalized to 50 IU/kg (AUC0-inf,norm).
Summary:
In paradigm™1, the estimated terminal half-life of N9-GP was 93 hours, 4.8 times longer than for patients’ previous product. For N9-GP, estimated incremental recovery at 30 minutes (IR30min) (1.33 IU/dL per IU/kg) was 94% and 20% higher compared with rFIX and plasma-derived FIX (pdFIX), respectively. AUC0-inf,norm with N9-GP was 10.1 times and 7.7 times higher compared with rFIX and pdFIX, respectively. Time to 3% and 1% FIX activities was 16.2 and 22.5 days, respectively. In paradigm™7, the estimated AUC0-inf,norm measured with one-stage clotting assay was 4.4 times higher for N9-GP compared with rFIXFc (9656 versus 2199 IU*h/dL). IR30min was 2.2 times higher (1.7 versus 0.8 IU/dL per IU/kg), maximum activity, dose normalized to 50 IU/kg, was 2 times higher (91% versus 45%), and FIX activity at 168 hours was 5.8 times higher (19% versus 3%). N9-GP had a longer terminal half-life (103.2 versus 84.9 hours; ratio: 1.22). Results were similar when measuring FIX activity with chromogenic assay. One patient in paradigm™1 developed transient hypersensitivity symptoms during administration of N9-GP and was excluded from PK analyses. No patient developed inhibitors in either trial, and no unexpected safety concerns were identified.
Conclusion:
These two single-dose PK trials show that N9-GP achieves higher FIX activity levels and greater AUC than pdFIX, rFIX, and rFIXFc through higher recovery and longer terminal half-life. These findings will support clinicians’ understanding of differences in PK between specific FIX products.
Annual Bleed Rates Compared Before and After Changing to Extended Half Life Products in Home Infusion Patients with severe hemophilia
NHF’s State Based Advocacy Coalitions (SBAC) Program
Long-term clinical outcomes of rFIXFc prophylaxis in adults 50 years of age or older with severe hemophilia B
Long-term clinical outcomes of rFVIIIFc prophylaxis in adults 50 years of age or older with severe hemophilia A
HOPE-B: Study design of a Phase III trial of an investigational gene therapy AMT-061 in subjects with severe or moderately severe hemophilia B
Joint health in patients with hemophilia A: analysis from the CHOICE survey
Do Hemophilia Treatment Centers Want Or Need A Regional Ethics Committee?
Identification of Challenges and Coping Strategies in the Management of Bleeding Disorders, From the Patient Perspective
Bringing families affected by Factor XIII deficiency together for a novel educational program
Factor X deficiency consumer education program’s inaugural year
Giving men with vwd a voice
Inhibitor Teams: building stronger connections and deeper learning
Understanding and finding symptomatic undiagnosed women
Introduction and Objectives:
Up to an estimated 1% of women in the United States have a bleeding disorder, but many with symptoms go undiagnosed. The National Hemophilia Foundation (NHF) conducted a needs assessment of currently diagnosed women to understand their path to diagnosis to help inform creation of an awareness campaign called Better You Know.
Materials and Methods:
In 2015, NHF fielded a survey of diagnosed women, yielding 184 responses. Informed by the needs assessment and input from a working group of medical providers and consumers, NHF launched the Better You Know campaign in 2016, which includes a website with a validated screening tool, resources on where to find providers on the path to diagnosis and treatment, outreach videos, social media posts, promotional postcards, paid media articles, accredited medical provider webinars, and mini-grants to select chapters for local outreach.
Results:
NHF found that women finally sought care for their symptoms for the following reasons: significant bleeding incident (surgery, childbirth, etc.), symptoms got too bad, or a family member was diagnosed. Women reported seeing the following providers first on their path to diagnosis: 38% hematologist; 23% primary care physician, 16% OB/GYN, and 15% pediatrician. About 80% of women also reported going to other people they know with a bleeding disorder for information and support. This lead to the creation of betteryouknow.org and other related campaign elements. From launch in July 2016 through October 2017, the website drew 4107 sessions, with 413 completing the screening tool and 86% of those being at risk. There were 108 clinicians who received accreditation for the provider webinars. NHF has developed partnerships with feminine hygiene product companies to spread the word, and pushes out campaign messaging via social media, chapters and some paid media. Total audience (website visits, social media impressions, etc.) for the campaign to date is over 252,500,000.
Conclusions:
Undiagnosed women with bleeding disorders face true challenges due to their bleeding symptoms. NHF will continue to raise awareness with providers and women, utilizing findings for effective methods of communication and education, through the Better You Know campaign.
Use of platelet microcapsule hybrids loaded with factor VIII to treat hemophilia A mice
The Relationship of Hope and Self-Compassion with Quality of Life among Individuals with Bleeding Disorders
Bleeding Disorders Education Day for School Nurses
Surgical Experience in Two Multicenter, Open-label Phase 3 Studies of Emicizumab in Persons with Hemophilia A with Inhibitors (HAVEN 1 and HAVEN 2)
Persons With Hemophilia Reinforce Their Desire to be More Active: US Findings From an International Patient Survey
BIVV001 – a novel, weekly dosing, VWF-independent, extended half-life FVIII therapy: first-in-human safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics
Patient perspectives on the value of reduced infusion frequency and longevity of protection for prophylactic treatment of hemophilia A
Retrospective review of unplanned hospitalizations and perceived pain in children and adults with a diagnosis of factor ten deficiency receiving home infusions of commercially available factor ten
Gender Differences in Parenting Stress and Social Support in Hemophilia Families
Real-world bleeding outcomes and adherence metrics among persons with hemophilia A and B receiving standard or extended half-life factor replacement products
Efficacy of on-demand treatment of bleeding episodes in hemophilia B patients with extended half-life N9-GP in pivotal trials: an in-depth analysis of treatment
Improving the screening for and evaluation of bleeding disorders in the primary care setting
An update on cognitive and behavior function in children and young adults with hemophilia: a 25-year journey from the Hemophilia Growth and Development Study to the current eTHINK study
Effects of Factor VIII Prophylaxis on Vascular Remodeling and Synovial Gene Expression Changes Associated with Hemarthrosis in FVIII-Deficient Mice
PROTECT VIII Extension Trial Interim Data: Safety of >5 Years of Treatment With BAY 94-9027
Effective Long-term Prophylaxis with BAY 94-9027 in Previously Treated Children: Interim Results of the PROTECT VIII Kids Extension Study
Long-term Benefit of BAY 81-8973 Prophylaxis in Children With Severe Hemophilia A: Interim Analysis of the LEOPOLD Kids Extension Study
Effective Protection for >5 Years With BAY 94-9027 Prophylaxis: PROTECT VIII Extension Trial Interim Results
BAY 94-9027 Maintains Hemostasis During Major Surgery in Adults and Adolescents With Severe Hemophilia A: PROTECT VIII Results
Achievement of therapeutic levels of factor VIII activity following gene transfer with valoctocogene roxaparvovec (BMN 270): Long-term efficacy and safety results in patients with severe hemophilia A
rFVIIIFc for immune tolerance induction in severe hemophilia A subjects with inhibitors: a follow-up retrospective analysis
Bypassing agent (BPA) use for the treatment of bleeds in persons with Hemophilia A (PwHA) with inhibitors before and after emicizumab prophylaxis in the HAVEN 1 study
Change in cost and units consumed by people with factor VIII and factor IX deficiency after switching from a standard half-life product to an extended half-life product
Patient Satisfaction with US Hemophilia Treatment Centers: National Trends 2017
Integrated efficacy and safety analysis of Phase 2 and 3 studies with glecaprevir/pibrentasvir in patients with a history of bleeding disorders and chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1–6-infection
Ultrasound-mediated Therapeutic Gene Transfer for Hemophilia
Discrepant Hemophilia A: Single Institution Experience
Pharmacokinetics, Efficacy, and Safety of High-Purity Factor X for Prophylactic Treatment of Hereditary Factor X Deficiency
A Multicenter, Retrospective Data Collection Study on the Compassionate Use of a Plasma-Derived Factor X Concentrate to Treat Patients with Hereditary Factor X Deficiency
My Life, Our Future: Development of the World’s Largest Genetic Research Repository for Hemophilia
Staying on TRAQ: Determining transition readiness from pediatric to adult care in adolescents and young adults with hemophilia
Qualitative findings from bleeding disorders camp
Camping programs for individuals with chronic illness are increasingly common. Unfortunately, few studies have been conducted to empirically evaluate whether camping programs are meeting their intended goals or having the positive outcomes that are expected of them. The current study was conducted as an evaluation of a bleeding disorder camp for patients with bleeding disorders and their siblings.
Participants in the current study included 77 participants, ages 7-20 (mean 11.58, SD = 3.21). The sample was 62.3% male and 63.6% patients (36.4% siblings). Most of the patients (52.6%) had severe bleeding disorders. Participants were administered the Children’s Hope Scale (CHS; Snyder et al., 1991), which evaluates two dimensions of hope (1. Agency, the ability to identify positive goals and 2. Pathways, the ability to find ways to meet identified goals) and overall hope. Participants demonstrated a significant improvement on the agency subscale of the CHS, t(35) = -2.16, p < .05. Participants reported qualitative aspects of living with bleeding disorders, including differences in their lives, aspects of their lives that are better, aspects about bleeding disorders that are often misunderstood, and advice for others with bleeding disorders. Responses to qualitative were analysed across groups (patients and siblings; severe and mild patients) and were found to be very consistent across these groups. This information has helped to provide information about experiences of youth affected by bleeding disorders and will be used to help inform upcoming camp programming. These findings have also demonstrated positive psychosocial outcomes associated with camp attendance.
Living with hemophilia B: examining quality of life and associated characteristics in the Hemophilia Utilization Group Studies (HUGS Vb) cohort
Efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics of once-weekly prophylactic emicizumab (ACE910) in pediatric persons (<12 years) with hemophilia A with inhibitors: interim analysis of single-arm, multicenter, open-label, phase 3 study (HAVEN 2)
Objectives:
Emicizumab, a novel bispecific humanized monoclonal antibody promotes coagulation by bridging FIXa and FX to replace the function of missing activated FVIII, and has potential to address unmet medical needs in pediatric persons with hemophilia A (PwHA) with inhibitors. This study assessed efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics of once-weekly subcutaneous emicizumab prophylaxis in pediatric PwHA with inhibitors.
Methods:
The study (NCT02795767) enrolled PwHA with inhibitors aged <12 years (or 12–17 years if <40 kg) previously treated with bypassing agents to receive emicizumab prophylaxis for ≥52 weeks. Emicizumab was administered subcutaneously at 3 mg/kg/week for 4 weeks, followed by 1.5 mg/kg/week thereafter. Efficacy objectives included bleed rate, and comparison of the bleed rate on emicizumab prophylaxis vs historical bleed rate obtained from a prospective, non-interventional study (NIS; NCT02476942). The NIS collected detailed, high-quality real- world data on bleeds and safety outcomes from a cohort of pediatric PwHA with inhibitors treated according to local, routine clinical practice. Participants from the NIS could subsequently enter the HAVEN 2 study, which permitted intra-individual comparisons.
Summary:
This interim analysis included 20 PwHA with inhibitors aged 3–12 years (median 8.5); 19 aged <12 years were included in the efficacy analyses. The median observation time was 12.1 weeks (range 7–14). In total, 18/19 (94.7%) participants had zero treated bleeds and 12/19 (63.2%) did not bleed while on study. Overall, 14 bleeds were reported in 7 participants, with none occurring in a joint or muscle. No participants have required up- titration of emicizumab. A substantial reduction in ABR on study vs ABR on prior treatment with bypassing agents (non-interventional study) was observed in 8 participants included in the intra-individual comparison; all 8 participants reported zero bleeds with emicizumab prophylaxis (efficacy period 85–99 days). Emicizumab was well tolerated; most common AEs were mild injection-site reactions (15%) and nasopharyngitis (15%). Three unrelated serious AEs were observed (mouth hemorrhage, appendicitis, catheter site infection). No thromboembolic or thrombotic microangiopathy events were reported. No anti-drug antibodies were detected. Mean trough emicizumab concentrations of >50 μg/mL were achieved after 4 loading doses of 3 mg/kg/week and sustained with maintenance doses of 1.5 mg/kg/week, and were consistent across age groups and body weight.
Conclusion:
Emicizumab prophylaxis was well tolerated and prevented/reduced bleeds in pediatric PwHA with inhibitors. Clinically meaningful reductions in ABR were observed compared with ABR on prior treatment with bypassing agents. The pharmacokinetic profile of emicizumab was similar to that seen in adolescent/adult PwHA with inhibitors. These interim data show the potential for emicizumab to reduce the disease and treatment burden for pediatric PwHA with inhibitors.
Efficacy, safety and pharmacokinetics of emicizumab (ACE910) prophylaxis in persons with hemophilia A with inhibitors: randomized, multicenter, open-label, phase 3 study (HAVEN 1)
Objectives:
Emicizumab, a bispecific humanized monoclonal antibody in development to address unmet medical needs in persons with hemophilia A with inhibitors (PwHAwI), bridges FIXa and FX to replace the function of missing FVIIIa, needed for effective hemostasis. This study assessed efficacy, safety and PK of emicizumab prophylaxis in PwHAwI.
Methods:
Study NCT02622321 was conducted at 43 centers/sites, and enrolled PwHAwI ≥12 y.o. Participants (pts) receiving prior episodic bypassing agents (BPAs) were randomized (2:1) to emicizumab prophylaxis vs no prophylaxis (Arm A vs B). Primary endpoint compared treated bleed rates in Arm A vs B. PwHAwI receiving prior prophylactic BPA received emicizumab prophylaxis in Arm C. Emicizumab was injected subcutaneously at 3 mg/kg/wk for 4 wks, and 1.5 mg/kg/wk thereafter.
Summary:
109 male PwHAwI were enrolled; median age 28 (range 12–75) yrs. Median (range) emicizumab treatment exposure was 24.0 (3.0–47.9) wk overall and 29.5 (3.3–47.9) wk in Arm A. Statistically significant, clinically meaningful reductions (87%) in treated bleed rates were observed between emicizumab prophylaxis vs no prophylaxis (Arm A vs B) (annualized bleeding rate [95% confidence interval] 2.9 [1.69 to 5.02] versus 23.3 [12.33 to 43.89], P<0.0001), and in all secondary bleed-related endpoints (spontaneous, joint, target joint, and all bleeds). Of note, a 79% reduction in treated bleed rate was seen with emicizumab prophylaxis (Arm C) vs BPA prophylaxis prior to study entry in a non-interventional study (NCT02476942; intra-individual comparison, P=0.0003). Overall, 67.3% of PwHAwI on emicizumab prophylaxis had zero treated bleeds. Statistically significant, clinically meaningful improvements in health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and health status were seen for Arm A vs B. Emicizumab was well tolerated. Total of 198 adverse events (AEs) were reported in 103 pts; most common AEs were injection-site reactions (15%), and 12 serious AEs were reported in 9 (8.7%) pts. Thrombotic microangiopathy and thrombosis (2 pts each in primary analysis) were reported and associated with high cumulative aPCC doses averaging >100 U/kg daily for >24 hr prior to event onset. No events occurred with emicizumab prophylaxis alone. Both TMA events resolved once aPCC treatment was stopped, and the thrombotic events did not require anticoagulation; 2 pts resumed emicizumab without sequelae (1 with TMA, 1 with thrombosis). No antidrug antibodies were detected. Mean trough emicizumab concentrations >50 μg/mL were achieved after 4 loading doses (3 mg/kg/wk) and sustained with maintenance doses of 1.5 mg/kg/wk.
Conclusion:
Emicizumab prophylaxis prevented or substantially reduced bleeds in PwHAwI and meaningfully improved HRQoL. Emicizumab had acceptable safety without excess thrombotic risk in the absence of concomitant aPCC. PK levels were sustained with once- weekly maintenance doses. These promising data could support a paradigm shift in the management and lives of PwHAwI.
What Symptoms of Hemophilia Most Impact Quality of Life – A Quantitative Survey of People Living with or Caring for Someone with Hemophilia A
A Cumulative Review on Four Decades of Thrombo-Embolic Events Reported with the Use of Activated Prothrombin Complex Concentrate (APCC) in Congenital Haemophilia
Estimating the prevalence of symptomatic, undiagnosed von Willebrand disease: analysis of medical insurance claims data
Assessment of numeracy, genetic knowledge and perceptions of genetic testing in carriers of Hemophilia A and B
Prevalence of gross motor delays in boys with hemophilia ages 4-14: single site study
Lessons Learned in the Assessment of Functional Status in US Adults With Hemophilia in the Pain, Functional Impairment, and Quality of Life (P-FiQ) Study: Importance of More Formalized Assessment of Function in the Comprehensive Care Setting
Lessons Learned From the Assessment and Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression in US Adults With Hemophilia in the Pain, Functional Impairment, and Quality of Life (P-FiQ) Study: Importance of Routine Screening and Comprehensive Approaches to Management
Lessons Learned in the Assessment of Pain in US Adults With Hemophilia in the Pain, Functional Impairment, and Quality of Life (P-FiQ) Study: Importance of More Formalized Discussions Around Pain in the Comprehensive Care Setting
Management of Hemophilia B in US Women and Its Impact on Education, Employment, and Activities: Results From the Bridging Hemophilia B Experiences, Results, and Opportunities Into Solutions (B-HERO-S) Study
The WFH Launches World Bleeding Disorders Registry to Expand Knowledge Base Worldwide
The WFH Annual Global Survey: Gender Distribution
Mild-Severe Hemophilia B Impacts Relationships for US Adults and Children With Hemophilia B and Their Families: Results From the Bridging Hemophilia B Experiences, Results, and Opportunities Into Solutions (B-HERO-S) Study
Impact of targeted education on obesity in children with hemophilia-a single HTC quality project
Real-World Specialty Pharmacy Dispensation and Expenditures Associated with Prophylactic Regimens Using Standard and Extended Half-Life Recombinant Factor IX Products in Severe Hemophilia B
Sports/Recreational Activity-Specific Range and Drivers of Risk in People With Hemophilia: Results of the Activity-Intensity-Risk (AIR) Survey and Consensus Meeting of US Physical Therapists
Physician practice patterns in the US show significant variation in how PK parameters are currently used to personalize care for US hemophilia A patients
Real-World Pharmacy Dispensation and Expenditures Associated with Standard and Extended Half-Life Recombinant Factor VIII Products in Hemophilia A
CHESS – Improving research and advocacy through an improved understanding of the economic and social burden of hemophilia
Assessing the Availability and Use of Resources to Support Youth with Hemophilia, their Families and Care Teams during Transition to Adult Health Care
Centralized Inhibitor Testing in the United States: Laboratory Methods Used for the Community Counts Registry for Bleeding Disorders Surveillance
Management of Bleed Events in the Phase 2 Study of Fitusiran, an Investigational RNAi Therapeutic Targeting Antithrombin for the Treatment of Hemophilia A and B with and Without Inhibitors
Fitusiran, an Investigational RNAi Therapeutic Targeting Antithrombin for the Treatment of Hemophilia A and B with and Without Inhibitors: Interim Results from a Phase 2 Extension Study
Management of Hemophilia Carriers Around The Time of Their Delivery: Phenotypic Variation Requiring Customization of Management
An Integrated Safety and Efficacy Analysis of Sofosbuvir-Based Regimens in Patients with Hereditary Bleeding Disorders
Efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of a high-purity plasma-derived factor X (pdFX) concentrate in the prophylaxis of bleeding episodes in children <12 years with moderate to severe congenital factor X deficiency (FXD)
Hereditary factor X (FX) deficiency in women and girls: treatment with a high purity plasma-derived factor X concentrate
Patient and Clinician Experience of Using Goal Attainment Scaling for Hemophilia (GAS-Hēm), an Innovative Patient-Centered Outcome Measure
Perceptions of Vulnerability, Protective Behaviors, and Reported Stress in Mothers of Sons with Hemophilia
Depression levels in patients with Hemophilia and von Willebrand
Bleeding disorders are a group of conditions that result when the blood cannot clot properly (American Society of Hematology, 2017). The most frequently occurring bleeding disorders include von Willebrand Disease (VWD), Hemophilia A, and Hemophilia B (FDA ́s, 2016).Some studies shows that is important to considered the depression in the psychological approach of patients with a bleeding disorder (Recht, Batt, Witkop, Gut, Cooper, Kempton, 2016 and Osorio, Bazán, Izquierdo, 2016). Beck ́s theory defined depression in cognitive terms. He saw the essential elements of the disorder as the “cognitive triad”: (a) negative view of self, (b) a negative view of the world, and (c) a negative view of the future. The depressed person views the world through an organized set of depressive schemata that distort experience about self, the world, and the future in a negative direction (Beck, A. 1972 in Lynn, P. 2015).
Objective:
Compare depression levels in groups of patients with haemophilia, Von Willebrand (VWD) and apparently healthy people.
Methods:
The study design was quantitative, non-experimental, transactional and correlational in which the difference between three groups of participants was analyzed: 41 patients with hemophilia A or B, 10 patients with VW and 20 apparently healthy people. The sample was obtained from Tabasqueña de Hemofilia A.C. through a non - random sampling of subjects - type. Depression symptoms were obtained by Beck ́s inventory and for control variables a questionnaire was applied. All of the findings were assessed by SPSS 21 for Windows program. Data were analysed using descriptive statistics, comparisons between groups were evaluated with Games-Howell coefficient and post hoc test.
Summary:
71 participants with a mean age of 28.24. Considering the patients who have a bleeding disorder, 74.50% of the sample was deficient of factor VIII, 11.76% of factor von Willebrand, 11.76% of factor VII and 1.96% of factor IX; 82.35% of them have access to treatment while 17.64 have not access. Statistically significant differences were found only in apparently healthy people compared to haemophilia patients (p=0.031). A marginal difference was detected between the group of apparently healthy people and von Willebrand patients (p=0.081).
Conclusions:
The presence of a coagulation disease increase the levels of depression and the severity of the symptoms.
Key Words: Hemophilia, Von Willebrand, Depression.
IMPACT QoL II - The relationship of depression and anxiety to control of chronic pain and adherence to clotting-factor treatment
PROTECT VIII: Can Eligibility for Less-Frequent Prophylaxis Dosing Regimens Be Predicted by Patient Characteristics?
Ethics of Compensated Plasma Donation
Assessment of Current Clinical Practices in Integrating Treatment Guidelines for Hemophilia
Verification of Effective Zika Virus Reduction by Production Steps Used in theManufacture of Plasma-Derived Medicinal Products
A Feasibility and Usability Study of a Nursing Orchestrated, Customized 3 Dimensional Virtual Reality Environment in Children with Hemophilia Undergoing Routine Intravenous Procedures
Optimal dosing strategies evaluated using a model of the terminal half-life curves for 11 rFVIII products
Characterization of Women and Girls with Hemophilia Treated in the US from A Claims Database
Updated results from a dose-escalation study in adults with severe or moderate-severe hemophilia B treated with AMT-060 (AAV5-hFIX) gene therapy: up to 1.5 years follow-up
Journey to Best Outcomes in Hemophilia Transition: Passage to Independence
Objectives:
To streamline and standardize the transition process of care through improved collaborations with staff and for persons with hemophilia transferring from a pediatric to an adult HTC. Processes were developed to provide patients with documented transition skills in order to foster medical independence in a complex healthcare environment.
Methods:
Continuous quality improvement tools were used to develop, implement and test a standardized transition tool for patients diagnosed with hemophilia A or B, ages fifteen to nineteen years of age. The transition tool was designed to assess the knowledge and skills of the adolescent in preparation for transition to adult care. Adherence to the administration of the tool in the pediatric HTC was the initial outcome measure. Key drivers included 1) improving communication between staff at the HTCs 2) transition tool development 3) educational resource content identification and 4) education of staff and families regarding the transition project. Communication was fostered through weekly team meetings to discuss and develop the transition tool in collaboration with the adult HTC. The adult HTC social worker would then attend the comprehensive clinic appointment at the pediatric HTC for those identified patients to assist in the preparation of transferring care. An excel spreadsheet, along with the ATHN database, was utilized to track patients to provide continuity of care during the transfer. Additionally, quarterly meetings were implemented with both HTC teams to discuss transferring patients and the continuum of the transition process. The transition tool was developed after review of available transition tools and was designed to provide systematic assessment of patient knowledge for transition readiness. The tool was refined through a series of PDSAs and implemented at each comprehensive clinic. The patient responses to the transition tool highlighted educational opportunities and led to the development of a resource cart to provide readily accessible targeted educational tools. Family and staff were educated about the value of transition readiness through team meetings, community outreach and during clinic visits.
Summary:
Use of the transition tool began in March 2016. Data was available through May 17, 2017. Thirty of 31 (97%) eligible patients completing the tool. Communication was improved between HTC teams. Educational tools were identified, obtained and provided to patients.
Conclusions:
We have successfully streamlined and standardized the transition process, identified educational opportunities and improved communication with staff at our HTCs utilizing established quality improvement techniques. Next steps include measurement of answered transition tool questions to further enhance patient/family knowledge and promote successful transition, as well as expansion to other age appropriate transition tools, to facilitate the journey to medical independence.
My Life Our Future Genotyping Days: On the Road Again to New Horizons
Pharmacokinetics and Prophylaxis Regimens and Relationship to Bleed Outcomes in Patients With Severe Hemophilia A Treated with BAY 81-8973
BAY 94-9027, a Site-Specifically PEGylated Recombinant Factor VIII: Preliminary Results From a Global Comparative Laboratory Field Study
Background:
Accurate measurement of factor VIII (FVIII) activity in patients with hemophilia A is important for patient monitoring and treatment decisions. Discrepancies in results using different assays or reagents to measure prolonged–half-life factor products have been recognized. BAY 94-9027 is a prolonged–half-life FVIII product site-specifically conjugated with a 60-kDa polyethylene glycol molecule (2×30 kDa branched).
Objective:
A global field study was conducted to assess the ability of clinical laboratories to measure BAY 94-9027 activity in spiked hemophilic plasma samples using their in-house or specific assays.
Design/Method:
In this 2-part study, laboratories received sample sets (3–4 per laboratory) of 26 blinded samples in randomized order for analysis. Each set consisted of triplicate test samples of BAY 94-9027 or a comparator (antihemophilic factor [recombinant] plasma/albumin-free method [rAHF-PFM (Advate® ); Shire]) spiked at low (<10 IU/dL), medium (10–50 IU/dL), and high (50–100 IU/dL) concentrations in pooled hemophilic plasma. Normal control plasma and unspiked hemophilic plasma in triplicate were positive and negative controls, respectively. Two additional blinded samples matching 2 of the other 24 samples in the set were included in each set to decrease the predictability of each set. Laboratories analyzed test samples using their in-house assays (one-stage, chromogenic, or both), reagents, and standards (part 1). In part 2, all laboratories tested 2 additional sample sets using 2 activated partial thromboplastin time kits (Pathromtin® and HemosIL® SynthASil) previously shown to accurately measure BAY 94-9027 and full-length FVIII. FVIII recovery and FVIII levels were primary and secondary endpoints, respectively.
Results:
Fifty-two laboratories in North America, Europe, and Israel participated in the study. In part 1, 49 laboratories tested samples using the one-stage assay, 16 used the chromogenic assay, and 13 used both assays. The reagents routinely used for measuring FVIII activity varied among participating laboratories. Mean FVIII recovery ranged from 75.1%‒103.2% for BAY 94-9027 and 94.6%‒114.7% for rAHF-PFM across all concentrations and reagents using the one-stage assay. As expected based on previously published data, the PTT-A and HemosIL® APTT-SP kits underestimated BAY 94-9027 at all concentrations. More accurate one-stage results were generated using the Pathromtin® and SynthASil kits, as shown in part 2 of the study. For the chromogenic assay, mean FVIII recovery ranged from 104.4%‒117.1% for BAY 94-9027 and 87.7%‒107.8% for rAHF-PFM across all concentrations.
Conclusion:
BAY 94-9027 can be accurately monitored using the chromogenic assay and select commonly used one-stage assay kits without need of a conversion factor.
Patient Reported Outcomes, Burdens and Experiences (PROBE) Study Data Visualization and Analysis
Addressing issues of women and girls with blood disorders (WGBD) through a collaborative obstetrics/gynecology, adult and pediatric hematology lifespan clinic: a pilot project
Attitudes and Perspectives on Ankle Function in People with Hemophilia: A Qualitative Study
Factors influencing uptake of evaluation among hemophilia carriers and potential carriers
A Study of Ethical Issues in the Bleeding Disorders Community (BDC)
Survey Finds Interest in Bleeding Disorder Social Work Specialty Credentialing
Chronicles of Caring: Nursing Stories from the Heart of Hemophilia
Access to Dental Care for People with Bleeding Disorders: Survey Results of Hemophilia Treatment Centers in the United States
Building ‘Zoris in the Sand’ – Best Practice for Bleeding Disorder Capacity Building in the Underserved US Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands
Intervention of Mexicans children and teenagers with hemophilia for their social integration
Adopting and Piloting the Patient Safety and Clinical Pharmacy Services Collaborative (PSPC) breakthrough model to transform and significantly improve adherence, improve health status and bring patients under control in the Hemophilia Community
Assessment of motor proficiency in people with bleeding disorders using the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency, Second Edition (BOT-2™)
Background:
Activity limiting joint disease has greatly decreased with the introduction of prophylactic treatment for people with severe bleeding disorders. Previous research using the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency, Second Edition (BOT-2TM), a standardized, normative, age and sex matched test of motor development, suggested motor development of males aged 4-21 years with bleeding disorders may be lower than age-matched peers.
Objective:
The primary purpose of this study was to compare the gross motor proficiency of boys with hemophilia ages 4-21 years followed at the Hemophilia Center at Oregon Health & Science University utilizing the BOT-2. Secondarily, we examined the relationship between joint health and gross motor proficiency.
Methods:
-
a) Participants and setting: Thirty-four subjects with either hemophilia A or B were recruited
from our center. Data collection occurred during clinic visits or at the patients’ homes.
-
b) Design and Procedures: A prospective, cross-sectional study design was used. The Upper Limb Coordination, Bilateral Coordination, Balance, Running Speed and Agility, and Strength subtests of the BOT-2 were administered. Body composition, range of motion, presence of an inhibitor, and use of prophylaxis were collected at the time of testing or from chart review.
-
c) Analyses: Analysis of variance (ANOVA) modeling was used to compare BOT-2 scores of PWH with baseline BOT-2 scores estimated from the general population of comparable age.
Summary:
Mean Running Speed & Agility scores were greater among boys with hemophilia compared to the control population (p=0.0026). Agility scores were similar between boys with hemophilia A and B (p>0.60), and significantly greater compared to the control group (p=0.0153). No other significant differences were found comparing boys with hemophilia to the control group. Within the boys with hemophilia cohort, age-adjusted ANOVA found no significant differences in BOT-2 scores between subjects of different severities, treatment regimen (prophylaxis or episodic), or diagnoses (Hemophilia A or B).
Conclusion:
Boys with hemophilia have the same or better gross motor proficiency as age matched peers.
Effect of hemophilia treatment center monitoring on bleeding rates
HEMO-milestones tool increases assessment of self-management competency and plan for skill building in patients with hemophilia
Update on a phase 1/2 open-label trial of BAX 335, an adeno-associated virus 8 (AAV8) vector-based gene therapy program for hemophilia B
An Evaluation of the Switch from Standard Factor VIII Prophylaxis to Prophylaxis with an Extended Half-Life, Pegylated, Full-length Recombinant Factor VIII (BAX 855)
Increased physical activity levels and improvement in treatment outcomes in patients who switch from on-demand to prophylaxis with BAX 855
SPACE (Study of Prophylaxis ACtivity, and Effectiveness): An interim descriptive analysis of patient activity levels and participation
Objective:
Personalizing treatment to a patient’s lifestyle and promoting overall health and wellness in persons with hemophilia (PWH) is essential to optimizing outcomes. There is limited evidence that correlates how activity and infusions impact bleeding episodes and further data on this relationship is needed. The research objective of SPACE is to prospectively explore the association between activity level, timing of infusion, and occurrence of a bleeding episode in PWH using novel technology.
Methods:
This six-month prospective, observational study includes PWH A or B in the United States currently receiving ADVATE or RIXUBIS between the ages of 13 and 65 years. Enrolled PWH use a smartphone eDiary application to log information on activities, infusions, and bleeding episodes. As an additional measurement of activity, enrollees are given a FitBit, a consumer-based activity tracker that measures steps taken and calories burned. Activity types are assessed based on their level of perceived risk for collision, according to the NHF “Playing It Safe” brochure. We report here current study status and descriptive analysis of baseline data.
Results:
The interim analysis included 15 patients with a median age of 19 (Range: 13 to 47). At baseline, 87% of patients were on prophylaxis and 13% treated on-demand treatment. Fifty-three percent of patients had 0 target joints at baseline. Eighty-seven percent of patients indicated that they had discussed activity participation with their physician. Sixty-seven percent of patients considered themselves ‘very satisfied’ or ‘satisfied’ with their level of activity. Data collected from the FitBit indicated that patients in SPACE walked on average 7,367 (SD: 3250) steps per day and burned 979 (SD: 398) calories from their activity. For patients on prophylaxis, the mean number of days per week doing mild, moderate and strenuous activity were 3.57, 2.64, and 1.5 respectively. Of the data reported on bleeding episodes, 40% of patients reported no bleeds at the time of the interim analysis. Forty percent of patients did not report having a bleed at the time of the interim analysis. Of all bleeds reported, 34% were associated with physical activity.
Conclusions:
Current data from SPACE demonstrates that subjects are active and participating in various activities. Continued data will provide better understanding of the types of activities and infusion schedules that may be associated with risk as well as protective effects on bleeding episodes by infusing prior to activity. A personalized approach to treatment based on physical activity levels may minimize bleeding risk in PWH.
Target Joint Spontaneous annualized bleed rate (sABR) Reduction: results from a pivotal trial of once weekly BeneFIX (nonacog alfa) in Hemophilia B subjects
Hemophilia B Patients Who Switch From rFIX to Extended Half-Life rFIX-Fc: A Retrospective Analysis of Cost using US Specialty Pharmacy Dispensing Data
My Life, Our Future: A “Genetics Day” to Facilitate Efficient Enrollment
Efficacy and safety of pdFX, a new high-purity factor X concentrate, in patients with mild to severe hereditary factor X deficiency undergoing surgery
Patient Preferences for FVIII and BAX 855: Results from the BAX 855 Pivotal Trial
Pharmacokinetics, safety, and efficacy of pdFX, a new high-purity factor X concentrate: a phase 3 study in patients with moderate or severe hereditary factor X deficiency
Objective:
To assess the pharmacokinetics (PK), safety, and efficacy of the first high- purity, plasma-derived factor X concentrate (pdFX) for on-demand treatment of bleeding episodes in a prospective, open-label, multicenter, nonrandomized phase 3 study in subjects with hereditary moderate or severe factor X (FX) deficiency (basal plasma FX activity <5 IU/dL).
Methods:
Included subjects were aged ≥12 years who required treatment with replacement therapy for ≥1 spontaneous or menorrhagic bleed in the past 12 months. Subjects received 25 IU/kg of pdFX on-demand for specific bleeds or as preventative use for 6 months to 2 years. PK was assessed following a single dose at baseline and after ≥6 months. Each bleed was categorized as major or minor, and subjects assessed efficacy for each bleed as “excellent,” “good,” “poor,” or “unassessable”; hospital- treated bleeds were also assessed by investigators. At study end, each investigator assessed the overall efficacy of pdFX. Safety assessments were adverse events (AEs), inhibitor development, viral seroconversions, and changes in laboratory parameters.
Summary:
The study enrolled 16 subjects (aged 12-58 years [mean 27.1 years], 62.5% female) with moderate (n=2) and severe (n=14) FX deficiency. PK parameters did not differ between baseline and repeat assessment visits, with overall mean (median, interquartile range [IQR]) incremental recovery of 2.00 (2.12, 1.79-2.37) IU/dL per IU/kg and half-life of 29.4 (28.6, 25.8-33.1) hours. In total, 468 pdFX infusions were administered; 187 bleeds treated with pdFX were analyzed for efficacy (98 major and 88 minor), of which 155 (82.9%) were treated with one pdFX infusion. A mean (standard deviation) of 1.2 (0.5) infusions per bleed were administered, with a median (IQR) dose of 25.0 (24.4-26.7) IU/kg. Efficacy of pdFX was rated as excellent in 90.9% of bleeds, good in 7.5%, and poor in 1.1%. For the 15 subjects who completed the study, investigators rated overall pdFX efficacy as excellent in 12 (80%) and good in 3 subjects (20%). Six mild/moderate AEs were observed, no serious AEs were considered by investigators to be possibly related to study drug, and no hypersensitivity reactions or clinically significant trends in any laboratory safety parameters were observed.
Conclusions:
In this study, pdFX was safe and efficacious in on-demand treatment of bleeds and short-term preventative therapy in subjects with moderate or severe FX deficiency at a nominal dose of 25 IU/kg. PK results supported these observed hemostatic effects.
Initial Observations From the Pain, Functional Impairment, and Quality of Life (P-FiQ) Study: Patient-Reported Outcome Assessments in US Adults With Hemophilia
Objective:
To assess pain and functional impairment through 5 patient-reported outcome (PRO) instruments in non-bleeding adults with hemophilia.
Methods:
Adult men with hemophilia (mild-severe) with history of joint pain/bleeding completed a hemophilia/pain history and 5 PROs (EQ-5D-5L with visual analog scale [VAS], Brief Pain Inventory v2 [BPI-SF], International Physical Activity Questionnaire [IPAQ-SF], SF- 36v2, and Hemophilia Activities List [HAL]) during routine visits. Initial patients were asked to complete the PROs again after their estimated 3-4 hour visit (retest population). PRO scores were calculated from published algorithms. Generally, higher scores indicate better health- related quality of life (HRQoL) and functional status, and greater pain severity/interference.
Summary:
381 Patients were enrolled between October 2013 and October 2014; 164 of the initial 187 completed the retest and are reported here. Median time for completion of the initial survey/PROs was 36.0 minutes and 21.0 minutes for the PRO retest. Most retest subjects had hemophilia A (74.4%) and were white-non-Hispanic (72.6%). Median (Q1, Q3) age was 33.9 (26.9, 46.0), 48.7% were married, 62.6% had some college or graduate education, 80.7% were employed, and 61.0% were overweight or obese. HCV (49.4%) was more common than HIV (16.5%); 61.0% self-reported arthritis/bone/joint problems. Median EQ-5D- 5L VAS was 80.0 (0-100 scale), and EQ-5D-5L health index 0.80 (-0.11-1 scale); 61.6% reported any problems with mobility (29.3% reported moderate/severe problems), 55.8% with usual activities (18.4% moderate/severe), and 22.0% with self-care (4.3% moderate/severe). 73.2% reported pain-discomfort (43.3% moderate/severe), and 41.1% anxiety-depression (14.7% moderate/severe). For BPI, median pain severity was 3.0 (0-10 scale) and pain interference 2.9 (0-10 scale); median worst pain was 6.0, least pain 2.0, average pain 3.0, and current pain 2.0. Pain most impacted general activity, mood, walking ability, and normal work, and least impacted relations with other people. Ankles were the most frequently reported site of pain. Median IPAQ total activity was 693.0 MET/min/week; 49.3% reported no activity in the prior week. Median SF-36v2 scores (0-100 scale) were lower for physical health (39.6) than for mental health (51.6). Median overall HAL score was 76.1 (0-100 scale); complex lower extremity activities were the most impacted activity domain.
Conclusions:
These 5 PRO instruments provide different levels of detail describing the impact of hemophilia on pain and function, and consequently, have varied burdens of administration. PRO data from the retest population demonstrate that most adults with hemophilia experience pain and functional impairment that impacts HRQoL, highlighting the importance of assessments and patient dialogue.
Development of a novel patient-centered outcome measure in hemophilia using Goal Attainment Scaling
Leading an Active Lifestyle with Hemophilia B: Estimating the Bleeding Risk with Different FIX Treatment Regimens
A Novel Anti-Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor Antibody, BAY 1093884, Restores Hemostasis in Induced Hemophilia A Rabbits With Reduced Thrombogenic Potential
Low Annualized Bleeding Rates in Phase 3 Studies of Recombinant Factor VIII Fc Fusion Protein (rFVIIIFc) in Subjects with Target Joints at Baseline
The impact of missing one or two infusions per month: a comparison of rFVIII and rFVIIIFc regimens
Hospitalization for Acute Bleeding Events among Individuals with von Willebrand Disease (VWD) in the United States
Description and Management of Pain and Functional Impairment in US Adults With Hemophilia: Initial Observations From the Pain, Functional Impairment, and Quality of Life (P-FiQ) Study
Cost of Treating Thrombotic Events in a US Population of Von Willebrand Disease Patients
Efficacy of a Recombinant Factor IX Investigational Product, IB1001 (trenonacog alfa) for Perioperative Management in Hemophilia B Patients
Objective:
To evaluate efficacy of IB1001 for perioperative management of bleeding under surgical circumstances in hemophilia B patients.
Methods:
The efficacy of IB1001 for perioperative management has been evaluated in a prospective, open-label, multicenter international study where 17 subjects (16 male PTPs and one female hemophilia B carrier) underwent 20 major surgical procedures. The PTPs were defined as patients with a minimum of 150 exposures to another factor IX preparation. The subjects had severe or moderately severe (factor IX level ≤ 2 IU/dL) hemophilia B without inhibitors, with exception of one mild hemophilia B female carrier. Efficacy of IB1001 was based on the surgeon’s assessment including estimation of blood loss as ‘less than expected’, ‘expected’, or ‘more than expected’ at the time of surgery and assessment of hemostasis at 12 and 24 hours post-surgery as ‘superior’, ‘adequate’, or ‘poorly controlled’. Transfusion requirements were also monitored.
Summary:
Thirteen major procedures in 12 male subjects were managed by bolus regimen, and 6 major procedures in 4 male subjects were managed by continuous infusion regimen. Mean loading dose for 13 major procedures managed by bolus regimen was 120 ± 11.4 IU/kg and mean maintenance bolus dose (given every 12 hours) was 59.7 ± 12.2 IU/kg. During the 24 hours following surgery, factor IX levels were successfully maintained over 60%, as intended. Factor IX levels at pre-infusion were 59.7% ± 15.9% at 12 hours after surgery and 54.4% ± 16.5% at 24 hours after surgery. For a major procedure in one female carrier, the bolus dose was 110 IU/kg, while the mean maintenance dose was 44.9 ± 7.0 IU/kg. Mean loading dose for 6 major procedures managed by continuous infusion regimen was 95.4 ± 14.5 IU/kg and the mean maintenance infusions were 7.1 ± 4.0 IU/kg/hr. In all major procedures, blood loss at the time of surgery was ‘expected’ or ‘less than expected’ as assessed by the surgeon. IB1001 was rated by the surgeon as ‘superior’ or ‘adequate’ in controlling hemostasis post-surgery, including 8 knee arthroplasties, two elbow arthroplasties, one knee amputation, one percutaneous Achilles tendon lengthening, one open inguinal hernia repair, one tibiotalar fusion, two arthroscopic synovectomies, three debridements and one total hysterectomy/bilateral oopherectomy. There were no transfusions required perioperatively.
Conclusions:
At the time of surgery, blood loss was expected or less than expected after IB1001 treatment, while post-surgery effective hemostasis control was achieved following IB1001 treatment in hemophilia B patients.
Efficacy of a Recombinant Factor IX Investigational Product, IB1001 (trenonacog alfa) in Previously Treated Patients with Hemophilia B
Personalization of Treatment Regimens for Physically Active Patients: A Comparison of Factor VIII and Extended Half-life Treatment Regimens
Changes in Child and Parent Ratings of Health-Related Quality of Life Among Children With Hemophilia A in the KIDS A-LONG study
Real-world dosing and patient characteristics of rFVIIIFc in hemophilia A patients
Objective:
To analyze real world rFVIIIFc patient characteristics and treatment interval patterns in patients with hemophilia A based on specialty pharmacy dispensing records.
Methods:
A retrospective analysis was conducted using aggregate Specialty Pharmacy Provider (SPP) records from July 2014 through Mar 2015. SPP data included 63 different attributes for each prescription, including trade name, NDC, quantity shipped, prescribed infusion dose, days supplied, and dose frequency. Patients were considered eligible for the analysis if they received at least one shipment of rFVIIIFc for a prophylactic treatment regimen. Patients were excluded from the analysis if they were being treated episodically, for immune tolerance induction, or pharmacy records did not specify a prescribed infusion dose. Patients were categorized according to their age and dosing interval.
Summary:
The analysis included 405 hemophilia A patients that received at least one shipment of rFVIIIFc with a median age of 23 (range: 2-68) and median weight of 70 kg (range: 10-154kg). Eight percent of dispensing records were for patients less than 6 years of age, 29% were between 6 and 17 years of age, and 63% were 18 years or greater. Pharmacy dispensing records represented 179 distinct prescribers across 40 states. Dosing frequency ranged from four times weekly to beyond once-weekly, with every four days as the most common dosing interval, representing 33% of patient records. The median infusion frequency was every four days. Fifty percent of all patients had a dosing frequency of four days or greater. Of the patients receiving rFVIIIFc that had previous rFVIII dispensing records, the most common rFVIII dosing frequency was three times per week. The majority of patients previously on prophylaxis regimen with a rFVIII dosing frequency of three times per week had a decreased number of prophylactic infusions per week on rFVIIIFc; 4% of patients reduced infusion frequency to every 3 days, 44% of patients reduced infusion frequency to twice weekly, 30% of patients reduced infusion frequency to every 4 days, 10% of patients reduced infusion frequency to every 5 days.
Conclusions:
Current SPP dispensing records demonstrate that rFVIIIFc is being used in a broad patient population based on age range and geographical distribution. Patients with hemophilia A in the US may experience reductions in FVIII infusion frequency when they switch to rFVIIIFc, with conversion to an infusion frequency every four days as the most common treatment regimen and the recommended prophylaxis starting dose according to the US Prescribing Information.
Quantitative research into people with hemophilia and caregiver perceptions of pre-filled solvent syringe (MixPro®)
Recombinant von Willebrand factor in severe von Willebrand disease: a prospective clinical trial
Kids B-LONG: Safety, Efficacy, and Pharmacokinetics of Long-Acting Recombinant Factor IX Fc Fusion Protein (rFIXFc) in Previously Treated Children with Hemophilia B
Objective:
Kids B-LONG was an open-label phase 3 study that evaluated the safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics (PK) of rFIXFc in previously treated children (aged <12 years; ≥50 prior exposure days [EDs] to FIX) with severe hemophilia B (≤2 IU/dL endogenous FIX) and no history of FIX inhibitors.
Methods:
Participants initiated prophylactic treatment with 50–60 IU/kg rFIXFc once-weekly; dose and interval adjustments were based upon PK data and bleeding frequency. The primary endpoint was development of inhibitors (neutralizing antibodies). Key secondary outcomes included PK and annualized bleeding rate (ABR).
Summary:
The study enrolled 30 participants (<6 years of age, n=15; 6 to <12 years of age, n=15); 90% completed the study. Prestudy, all participants received FIX prophylaxis (23/30 were dosing ≥2x/week). The median time on study was 49.4 weeks; 24 participants had ≥50 rFIXFc EDs. No participant developed inhibitors to rFIXFc. The pattern of adverse events reported was typical of the population studied. There were no serious allergic reactions and no thrombotic events. No serious adverse events were assessed by the investigator as related to rFIXFc. The terminal half-life (geometric mean [95% CI]) of rFIXFc was 66.5 (55.9, 79.1) hours in the <6 years cohort (n=11) and 70.3 (61.0, 81.2) hours in the 6 to <12 years cohort (n=13). The geometric mean (95% CI) half-life of prestudy BeneFIX was 18.2 (15.5– 21.3) hours in the <6 years cohort (n=11) and 19.2 (17.6–20.9) hours in the 6 to <12 years cohort (n=9). Median (IQR) ABR was 1.97 (0.00, 3.13) overall, and 0.00 (0.00, 1.16) for spontaneous bleeds; 33.3% of participants reported no bleeds on study. At study end, 97% of participants were dosing once weekly. The median (IQR) total weekly prophylactic dose with rFIXFc was 59.4 (53.0, 64.8) IU/kg and 57.8 (51. 7, 65.0) IU/kg, in the <6 years and 6 to <12 years cohorts, respectively. The prestudy FIX median (IQR) total weekly prophylactic dose was 110.0 (58.0, 188.0) IU/kg and 100.0 (58.0, 120.0) IU/kg in the <6 years and 6 to <12 years cohorts, respectively. 75.0% of bleeding episodes were controlled with 1 infusion; 91.7% with 1 or 2 infusions (median average dose per infusion: 68.22 IU/kg).
Conclusions:
rFIXFc was safe and effective for the prevention and treatment of bleeding in children with severe hemophilia B. Study participants achieved low bleeding rates with extended-interval rFIXFc prophylaxis, while reducing their weekly prophylactic factor consumption compared with their prior FIX regimen.
The Effects of Hemophilia on Socialization
Global Knowledge and Confidence Assessment of Hemophilia Clinical Practice Approaches Among Pediatricians
A Novel Anti-Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor Antibody, BAY 1093884, Prevents Bleeding in Hemophilia A Mice
Background:
BAY 1093884 is a fully human monoclonal antibody against tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) developed as a bypass agent for hemophilia patients with inhibitors. It restores thrombin burst for stable clot formation in hemophilic conditions in vitro.
Aims:
The goal of this study was to elucidate the in vivo prophylactic hemostatic potency of BAY 1093884.
Methods:
The hemophilia A mouse tail vein transection model was used for this study to mimic the venous bleeding characteristics of severe hemophilia. Male hemophilia A mice (n=12/group) were treated prophylactically with escalating doses of BAY 1093884. All treatments were administered as single intravenous (IV) bolus at 4 different time courses prior to injury (1, 3, 5, and 7 days). Bleeding was induced by a 1.2-mm deep incision across the left lateral vein. Following injury, the animals were monitored hourly for moribundity for up to 9 hours and after 24 hours followed by euthanasia.
Results:
Efficacious doses of BAY 1093884 providing 50% protection for survival (ED50) for up to 6 days after IV bolus ranged from 0.6–2 mg/kg. In comparison, only 25% protection was achieved 6 days after the treatment with a very high dose of 1000 IU/kg of recombinant factor VIII (rFVIII). The effect of a single IV dose of 18 mg/kg BAY 1093884 providing 80%–90% survival was maintained over 8 days (ED50 6 mg/kg), whereas a single IV dose of rFVIII failed to provide protection over an 8-day period.
Conclusions:
These studies demonstrate that BAY1093884 prevents bleeding and increases long-term survival to a greater degree than rFVIII in hemophilia A mice and may offer a convenient prophylactic treatment option for hemophilia patients with inhibitors.
Reduced Polyethylene Glycol–Conjugated B-Domain–Deleted Factor VIII (PEG-BDD-FVIII) Clearance: Selective PEG Steric Modulation Without Affecting Potency
Pegylated full-length recombinant factor VIII (BAX 855) for prophylaxis in previously treated adolescent and adult patients with severe hemophilia A
Long-term safety and prophylactic efficacy of once-weekly subcutaneous administration of ACE910 in Japanese hemophilia A patients with and without FVIII inhibitors: Interim results of the extension study of a phase I study
Relative Health Status of Young Adults in the Hemophilia Utilization Group Studies (HUGS)
Associations Between Annual Bleeding Episodes and Financial Burden of Illness Among Persons with Hemophilia A and B in the United States
Long-term safety and efficacy of recombinant factor VIII Fc (rFVIIIFc) for the treatment of severe hemophilia A: United States subgroup interim analysis of the ASPIRE study
Objective:
The ongoing rFVIIIFc extension study, ASPIRE (clinicaltrials.gov #NCT01454739), evaluates the long-term safety and efficacy of rFVIIIFc in adults, adolescents, and children with severe hemophilia A. Here we report interim outcomes for United States (US) subjects in ASPIRE.
Methods:
Eligible subjects could enroll in ASPIRE upon completing A-LONG or Kids A-LONG. There were 4 treatment groups: individualized prophylaxis (25-65 IU/kg every 3-5 days, or 20-65 IU/kg on D1, 40-65 IU/kg on D4 if twice weekly); weekly prophylaxis (65 IU/kg every 7 days); modified prophylaxis (to further personalize and optimize treatment when needed); or episodic treatment. Subjects could change treatment groups at any time. Subjects <12 yrs participated only in individualized and modified prophylaxis groups. Primary endpoint: development of inhibitors. Secondary outcomes included annualized bleeding rate (ABR) and rFVIIIFc exposure days (EDs).
Summary:
Sixty subjects (49 from A-LONG; 11 from Kids A-LONG) enrolled. As of the interim data cut (6 Jan 2014), the median time on ASPIRE was 80.37 (A-LONG) and 15.94 (Kids A-LONG) wks; 82% (A-LONG) and 27% (Kids A-LONG) of subjects had ≥100 cumulative rFVIIIFc EDs. 7/49 A-LONG subjects changed treatment groups upon enrollment into or during ASPIRE; 2 Kids A-LONG subjects switched from individualized to modified prophylaxis upon enrollment into ASPIRE. Median ABRs were low with rFVIIIFc prophylaxis (Table). Overall, most subjects treated prophylactically during the parent study did not experience changes to their total weekly prophylactic dose or dosing interval during ASPIRE. For subjects who enrolled from A-LONG and Kids A-LONG, 94% and 100% of all bleeding episodes during ASPIRE, respectively, were controlled with 1 infusion. In the overall study population, no inhibitors were observed during ASPIRE; adverse events were typical of the general adult and pediatric hemophilia A populations.
Conclusion:
Interim data from US subjects in ASPIRE are consistent with those of the phase 3 parent studies and the overall ASPIRE interim analysis. Results from ASPIRE confirm the longer-term safety of rFVIIIFc and the maintenance of a low ABR with extended interval prophylactic dosing in individuals with severe hemophilia A.
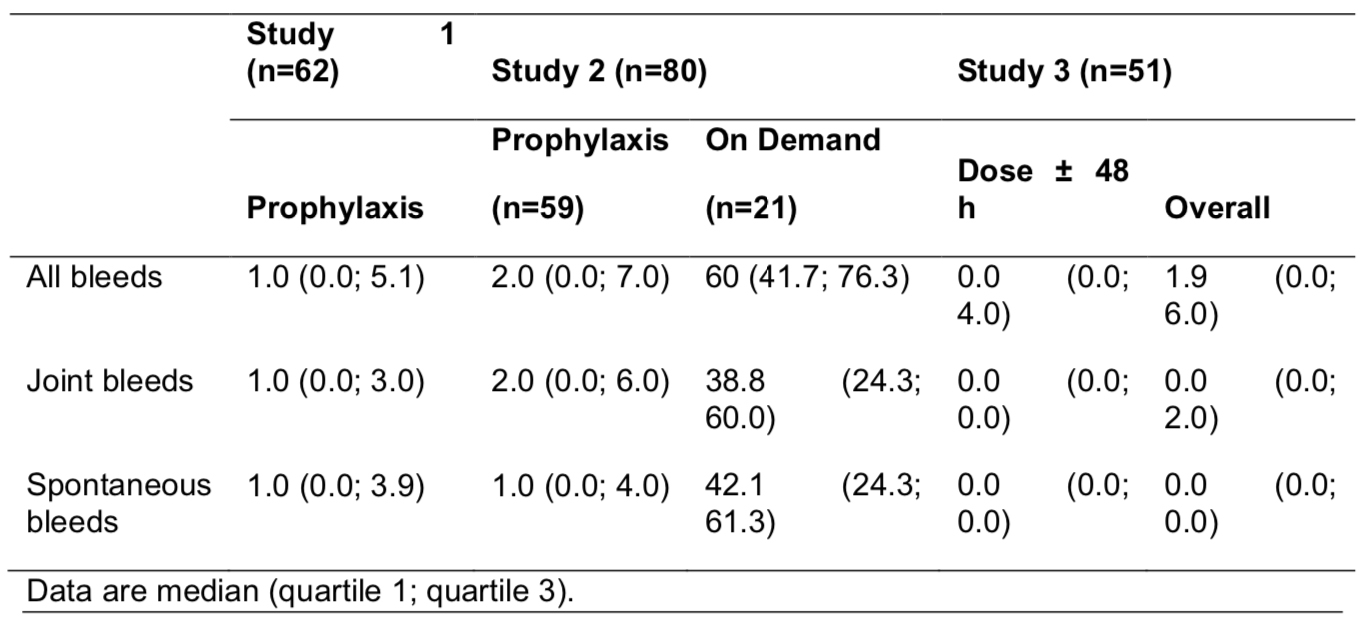
Increase or Maintenance of Physical Activity in Patients Treated with Recombinant Factor IX Fc Fusion Protein (rFIXFc) in the B-LONG and Kids B-LONG Studies
Patients Treated with Recombinant Factor VIII Fc Fusion Protein (rFVIIIFc) Reported Increased or Maintained Physical Activity in the A-LONG and Kids A-LONG Studies
Patient Satisfaction with US Hemophilia Treatment Centers 2015: National Results
Objective:
Patient satisfaction with healthcare services enhances patient experience, improves outcomes, and is increasingly mandated by public and private payers. While many US Hemophilia Treatment Centers (HTC) periodically assess patient satisfaction, the lack of a uniform survey hampered national measurement. To remedy this knowledge gap, the US HTC Network implemented a national patient satisfaction survey in 2015.
Methods:
A Regional HTC Coordinator workgroup devised, piloted, and finalized a two-page survey for self-administration online, at clinic, or at home, in English or Spanish and mailed to households. Survey content and format were based on national health surveys to enhance comparability and scientific robustness, informed by legacy regional HTC surveys. Questions assessed patient demographics; satisfaction with services, team members, and care processes; and Healthy People 2020 adolescent transition objectives. Surveys included open ended questions to obtain qualitative data. Respondents were anonymous but identified with their respective HTCs. Participation was voluntary. Persons with genetic bleeding disorders who had HTC contact in 2014 were eligible. During February 2015, 124/130 HTCs sent surveys to 27,563 households. Parents completed surveys for children under age 15. No reminders were sent. Data were entered and analyzed at a central site and aggregated at national, regional and HTC levels.
Results:
Over 4800 households (17.4%) returned surveys by April 30, 2015. National analyses on 4332 surveys reveal that 96.6% were ‘always’ or ‘usually’ satisfied with HTC care. Over 80% were ‘always’ satisfied with the core HTC team members. Three quarters of 12-17 year olds were ‘always’ satisfied with HTC encouragement regarding becoming more independent, and how the HTC discussed caring for a bleeding disorder upon reaching adulthood. Eighty– 90% were ‘always’ or ‘usually’ satisfied with care processes, e.g. shared decision making, care coordination, ease of obtaining timely information and services, and being treated respectfully. Insurance and language were ‘always’ a problem for 20%. 29.0% of respondents were female and 10.3% Hispanic. 83.4% were Caucasian, 5.8 African- American, 3.1% Asian/Pacific Islander or Native Hawaiian, 4.3% Multiple races, and 4% Other. Over half had severe or moderate FVIII or FIX deficiency or VWD Type 3. Ages ranged from newborns to 96 years: 38% under 18, 20% age 18 – 34, and 42% over age 35.
Conclusions:
Implementing a National Patient Satisfaction Survey for the US HTCN is feasible, and provides valuable information. Satisfaction with HTC services is high, but insurance and language ‘always’ pose problems for one fifth. Further analyses will examine regional differences.
Impact of FVIII CRM-positive status on the immunogenicity of FVIII in the hemophilia A mouse model
BAY 81-8973: Safety Observations in Clinical Trials in Adults, Adolescents, and Children With Severe Hemophilia A
Introduction:
BAY 81-8973 is Bayer’s new full-length recombinant factor VIII (FVIII) product in development for the treatment of hemophilia A. BAY 81-8973 has no human- or animal- derived raw materials added to the cell culture, purification, or formulation processes.
Objective:
To evaluate the safety profile of BAY 81-8973 as documented in clinical trials with BAY 81-8973.
Methods:
The safety of BAY 81-8973 for prevention and treatment of bleeds in patients with severe hemophilia A (<1% FVIII) was evaluated in 3 clinical studies: 2 in adolescent and adult previously treated patients (PTPs; aged 12–65 years with ≥150 previous exposure days [EDs]) and 1 in pediatric PTPs (aged ≤12 years with ≥50 previous EDs). A total of 193 PTPs (including 51 pediatric patients) were included to assess the frequency of adverse reactions in the 3 phase 3 studies. The immunogenicity of BAY 81-8973 was also evaluated in PTPs. Adverse reactions were collected and analyzed throughout the studies.
Results:
The frequency, type, and severity of adverse reactions in children were similar to those in adults. Adverse reactions in PTPs are listed in Table 1. In PTPs evaluated to date for immunogenicity, no inhibitors were detected.
Table 1. Adverse Reactions in Previously Treated Patients (N=193)
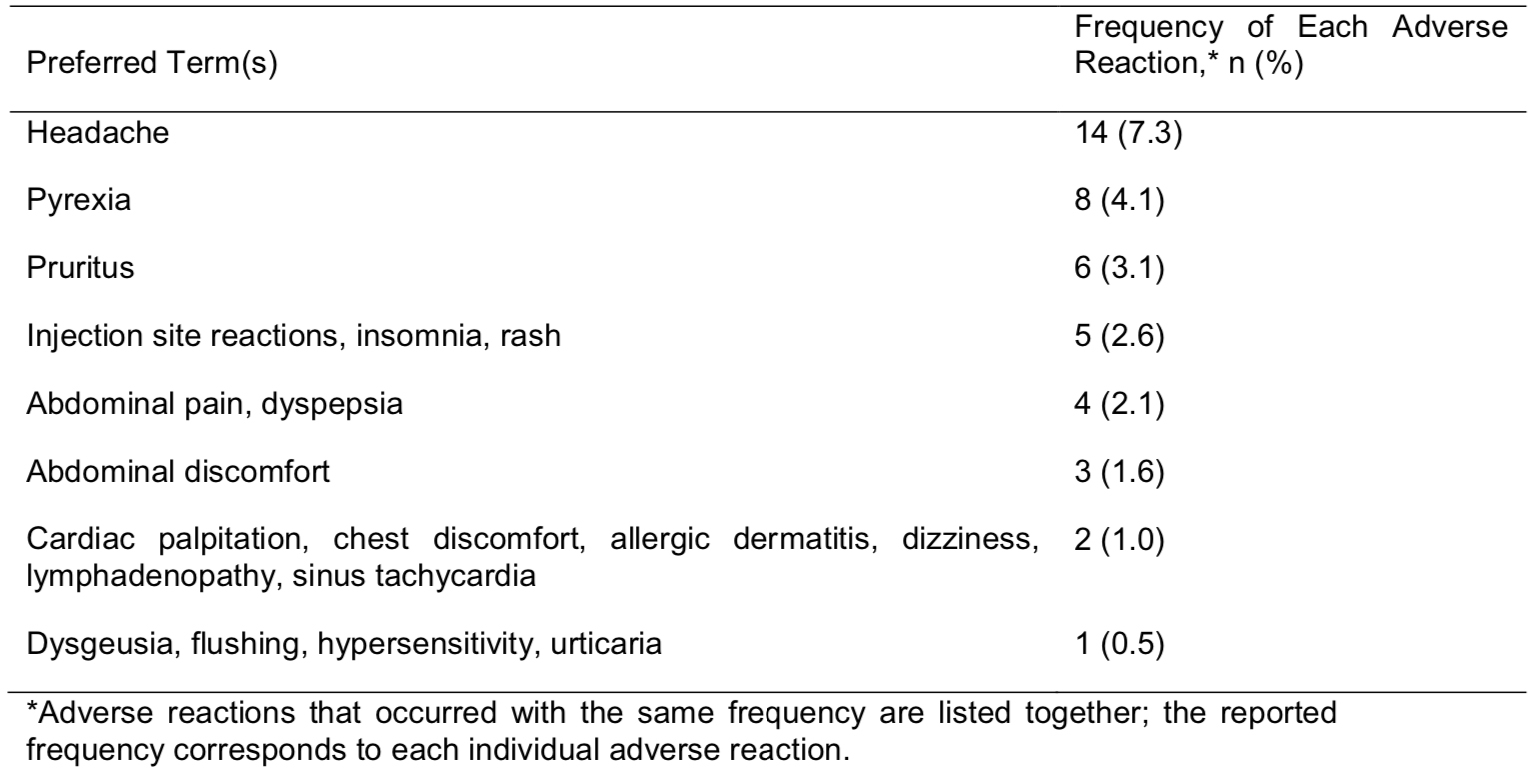
Conclusions:
The incidence of treatment-related adverse and serious adverse reactions in the BAY 81-8973 trials was low (<10%) and similar to those reported in the literature for other full-length FVIII products. No PTP developed a FVIII inhibitor.
A Half-Life Extended Fusion Peptide Inhibitor of TFPI Improves Hemostasis in Preclinical Models of Hemophilia
Objective:
TFPI is a potent inhibitor of the tissue factor (TF)-induced extrinsic pathway of coagulation. Inhibition of TFPI with antibodies, aptamers, or peptide inhibitors improves hemostasis and may become an option for non-i.v. treatment of patients with hemophilia including those with inhibitors.
Method:
We developed a TFPI inhibitory fusion peptide (FP) consisting of a linear and a cyclic peptide connected by an optimized linker. The two peptides bind to different epitopes on TFPI and synergistically inhibit TFPI. The FP was further improved by half-life extending (HL) non-covalent albumin binding. HL-FP was characterized for in vitro inhibition of TFPI, pharmacokinetics, and improvement of coagulation in animal models of hemophilia.
Results:
HL-FP bound to and efficiently inhibited TFPI in several in vitro test systems. The binding affinity of < 1nM correlated well with inhibition of TFPI in model assays, resulting in IC50s of ~0.7nM. HL-FP efficiently inhibited plasma TFPI, which improved all thrombin generation (TG) parameters in hemophilia A and B patient plasma (EC50s of 6 to 20nM). HL-FP increased peak thrombin levels of hemophilia plasma to a range established for individual normal plasma. Assays were also carried out at flTFPI concentrations up to 10nM, which is 40- to 50- fold above normal. Increased TFPI levels may occur locally upon platelet activation. HL-FP efficiently neutralized elevated TFPI, raising TG to levels observed for inhibition of physiologic TFPI concentrations. Non-covalent binding to albumin substantially increased the half-life to ~4 h with ~50% s.c. bioavailability in mice. The ex vivo procoagulant activity determined by TG correlated well with HL-FP plasma concentrations. In a repeated dose study, the HL-FP was well tolerated and did not accumulate TFPI, indicating that HL-FP did not interfere with TFPI clearance. HL-FP significantly reduced bleeding in the hemophilia mouse tail cut model at a dose as low as 40 nmol/kg. In marmoset monkeys, HL-FP efficiently improved ex vivo plasma TG, even at low peptide plasma concentrations (25-55nM).
Conclusion:
To summarize, we developed a TFPI inhibitor composed of two TFPI antagonistic peptides that completely inhibits TFPI. Introduction of an entity non-covalently binding to albumin provides intermediate half-life extension and s.c. bioavailability. This HL-FP improved coagulation and hemostasis in animal models of hemophilia, did not interfere with TFPI clearance receptor interactions, and efficiently neutralized elevated TFPI. Our HL-FP appears to be useful in preventing bleeding in hemophilia, and provides a FVIII and FIX independent approach for non-i.v. treatment.
Prevalence of high BMI in school age children with hemophilia
BAY 81-8973: The Effects of Routine Prophylaxis on Total, Joint, and Spontaneous Bleeding in Adolescents, Adults, and Children With Severe Hemophilia A
Introduction:
BAY 81-8973 is Bayer’s new full-length recombinant factor VIII (FVIII) product for the treatment of hemophilia A, with no human- or animal-derived raw materials added to the cell culture, purification, or formulation process.
Methods:
The safety and efficacy of BAY 81-8973 for routine prophylaxis in patients with severe hemophilia A (<1% FVIII) was evaluated in 3 clinical studies: 2 in adolescent and adult previously treated patients (PTPs; aged 12–65 years [Study 1 and Study 2]) and 1 in children aged ≤12 years (PTPs: completed [Study 3]; previously untreated patients: ongoing), enrolling a total of 204 patients. In Study 1, the prophylaxis regimen was 20–50 IU/kg 2x–3x/wk as determined by the investigator. In Study 2, patients were randomized to prophylaxis (20–30 IU/kg 2x/wk or 30–40 IU/kg 3x/wk) or on-demand treatment. In both 12-month studies, the primary efficacy variable was the annualized bleeding rate (ABR). In Study 3, the prophylaxis regimen was 20–50 IU/kg 2x–3x/wk or every other day, as determined by the investigator, for ≥50 exposure days (approximately 6–8 months). The primary efficacy variable was the ABR for total bleeds occurring within 48 hours of previous prophylaxis treatment; ABR was also analyzed independent of time of injection.
Results:
A total of 193 patients treated with BAY 81-8973 were included in the analysis (Table 1). Sixteen (25.8%), 16 (27.1%), and 23 (45.1%) patients treated prophylactically had 0 bleeding episodes in Studies 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
Table 1. Annualized Bleeding Rates
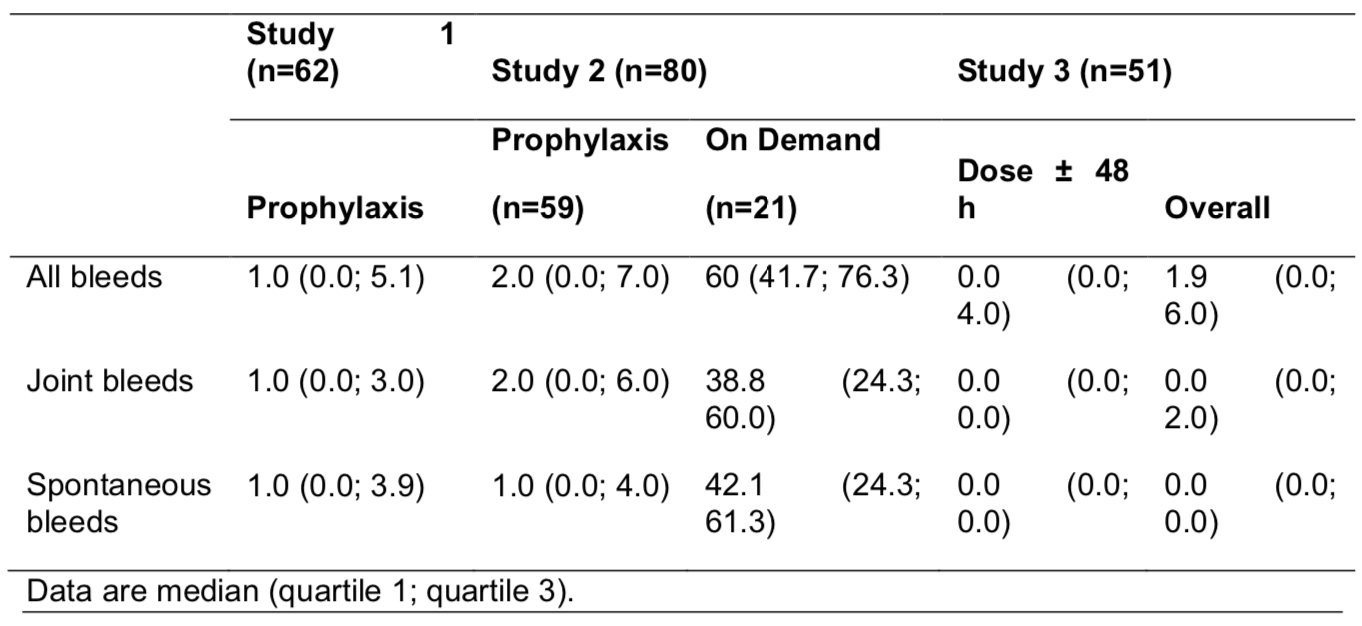
Conclusions:
Study 1 and Study 2 demonstrated the efficacy and safety of routine prophylaxis treatment with BAY 81-8973 in adolescents and adults. Study 2 also demonstrated the superiority of prophylaxis over on-demand treatment during a one-year treatment period. An additional study in children aged ≤12 years showed low annualized rates for all bleeds, joint bleeds, and spontaneous bleeds within 48 hours after injection or later during routine prophylaxis.
SPINART 3-Year Analyses: Patient- and Joint-Level Changes in Colorado Adult Joint Assessment Scale and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scores With Bayer’s Sucrose-Formulated Recombinant Factor VIII (rFVIII-FS) in Adolescents and Adults
Introduction:
Efficacy and safety of routine prophylaxis vs on-demand treatment with Bayer’s sucrose-formulated recombinant factor VIII (rFVIII-FS) in patients with severe hemophilia A were evaluated in the randomized, controlled SPINART study.
Aim:
Patient- and joint-level changes at year 3 in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and Colorado Adult Joint Assessment Scale (CAJAS) scores were compared to investigate if individual joint data revealed results that may have been obscured in previously reported patient-level analyses.
Methods:
SPINART included males aged 12–50 years with severe hemophilia A, ≥150 exposure days to FVIII, no inhibitors, and no prophylaxis for >12 months in the past 5 years. Patients were randomized 1:1 to rFVIII-FS on demand or prophylaxis (25 IU/kg 3x/wk). Changes from baseline to year 3 were evaluated for 6 index joints (knees, ankles, elbows) using the Extended MRI (eMRI) scale and CAJAS. Percentages of patients or joints with improved, unchanged, or worsened scores were evaluated.
Summary:
Of the 84 patients in SPINART, eMRI and CAJAS change from baseline data were available for 62 (prophylaxis, n=32; on demand, n=30) and 76 patients (n=39; n=37) and for 386 (n=197; n=189) and 446 joints (n=224; n=222), respectively. Categoric analysis of CAJAS data at year 3 showed a higher percentage of patients treated prophylactically vs on demand with improved scores (64.1% vs 43.2%) and a lower percentage with worsened scores (28.2% vs 51.4%); with eMRI, the percentage improved was smaller (12.5% vs 6.7% improved; 75.0% vs 73.3% worsened). At individual joints, improved, unchanged, and worsened CAJAS scores in patients treated with prophylaxis vs on demand were 46.0% vs 33.3%, 22.3% vs 24.3%, and 31.7% vs 42.3%; eMRI values were 8.1% vs 3.7%, 61.9% vs 69.8%, and 29.9% vs 26.5%.
Conclusions:
These data suggest that in adults and adolescents with severe hemophilia A, joint function as measured by CAJAS is more likely to improve after 3 years of routine prophylaxis with rFVIII-FS than joint structure as measured by MRI.
BAY 81-8973: Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Adolescents, Adults, and Children With Severe Hemophilia A
Long-term safety and efficacy of recombinant factor IX Fc (rFIXFc) in adults and adolescents with severe hemophilia B: interim results of the B-YOND study
Interim results of the B-YOND study evaluating long-term safety and efficacy of recombinant factor IX Fc (rFIXFc) in children with severe hemophilia B
Adherence influences annualized bleeding rate during prophylaxis with turoctocog alfa: results from the guardian™1 trial
Pediatric Venous Thrombosis Associated With Staphylococcal Infections: A Single Institutional Experience
Pharmacist/Provider Collaboration needed to Optimize Dosing Regimens in Order to Reduce Bleed Rates in Hemophilia A Patients on Prophylaxis Regimens
Varying Regimens in Hemophilia A Patients Undergoing Immune Tolerance: Removing Barriers to Enhance Outcomes
Swimming exercise ameliorates pain, swelling and bone quality in a blood-induced joint damage animal model
Hemophilia Genotyping Results from the My Life, Our Future Project
Haemophilia A Carriers Experience Reduced Health-Related Quality of Life
Comorbidities among Adults with Hemophilia: Hemophilia Utilization Group Studies (HUGS V)
Does Quality of Life improve with successful immune tolerance induction? An illustrative case report.
A Comparison of US Prophylaxis Rates Shows Lower Prescribing for Severe Hemophilia B Patients than Severe Hemophilia A Patients
Changes in Healthcare Resource Utilization and Haemophilia Related Events in Patients Diagnosed with Haemophilia A
Addressing patient concerns about product switching in hemophilia A: Evaluating turoctocog alfa data from the guardian™ clinical trial program
Treatment, Outcomes, and Access to Care Among Young Adults (ages 18-30) With Hemophilia in the US Hemophilia Experiences, Results and Opportunities (HERO) Study
Hemophilia impacts relationships and employment of young adults (ages 18-30) in the us hemophilia experiences, results and opportunities (hero) study
Pain and Arthropathy Impact Quality of Life of Young Adults With Hemophilia (ages 18-30) in the United States: Observations From the Hemophilia Experiences, Results and Opportunities (HERO) Study
Objective:
To assess quality of life, self-reported comorbidities, health-related quality of life (HRQoL), and impact of hemophilia on activities of young adult (YA) patients with hemophilia (PWH).
Methods:
Analysis of US YA-PWH respondents (aged 18-30) in the international HERO study conducted in 2010-2011. US respondents were recruited through NHF, Facebook, and e-mail. An independent ethics board approved the US survey.
Summary:
Of 189 adult PWH HERO respondents in the United States, 66 were aged 18-30 years, 74 were aged 31-40 years, and 49 were older than 40 years. The median (interquartile range) age of YA-PWH was 26 (22-28), and had hemophilia A (58%), hemophilia B (21%), or hemophilia with inhibitors (21%). Most were Caucasian (77%). Half were on prophylaxis (50%), with the remainder treated on-demand alone (24%) or with occasional short-term prophylaxis (24%). Compared with PWH older than 40 years, YA-PWH less frequently self- reported bone/skeletal/arthritis (41% vs 67%), chronic pain (38% vs 57%), and viral comorbidities (20% vs 65%). On EQ-5D-3L, 62% of YA-PWH reported no difficulties with mobility, 71% no difficulties with usual activities, and 94% no difficulties with self-care. In contrast, 68% reported moderate and 5% extreme pain/discomfort, and 33% reported some/moderate and 8% extreme anxiety/depression. On EQ-5D-VAS, 53% reported VAS scores of 80-90-100 (vs 24% for PWH >40 years). Surprisingly, 89% reported pain interference with daily activities in the past 4 weeks, with 9% reporting it was extreme/a lot. More YA-PWH had pain only with bleeding than PWH older than 40 (42% vs 18%), with 14% citing pain all the time and 39% reporting pain all the time and worse with bleeding. YA-PWH reported seeking psychological treatment in the prior 5 years (26%), frequently related to hemophilia (71%). When asked about specific activities, YA-PWH reported participating in lower-risk (80%), intermediate-risk (61%), and higher-risk activities (27%); older PWH reported 82%, 45%, and 16%, respectively.
Conclusions:
YA-PWH in the United States are less likely than older PWH to report arthritis, chronic pain, or viral diseases; yet, HERO results suggest these remain important problems for this age group. Pain appears to be perhaps the most significant; only 11% did not report pain interference in the past 4 weeks, and only 27% reported no pain/discomfort at the time of the survey. Additionally, 33% reported some/moderate depression. The relationship of intermediate- and high-risk activities to the rates of reported pain and arthritis is unclear.
Real World Utilization and Cost of aPCC versus rFVIIa Among Hemophilia Patients with Inhibitors in the US
Ongoing Prospective ADVATE Immune Tolerance Induction Registry (PAIR) Continues to Demonstrate Success Rates Consistent with Published Literature
The use of combination therapy with plasma derived and recombinant factor VIII in patients with hemophilia A: a single institution experience
New insights from modeling FVIII Kinetics of Native vs. Extended Half-life FVIII Products - Comparing FVIII Coverage under Various Dosing Scenarios
Using Oral History for Patient Education: The Gift of Experience II: Conversations with Parents about Hemophilia
The expression of codon-optimized blood coagulation factor VIII using a lentiviral system
The Impact of Reduced Treatment Frequency: Qualitative Evaluation of Adherence and Outcomes in Chronic Disease Management
Bleeding Risk for the Active Person with Hemophilia: A Comparison of Factor VIII Treatment Regimens
Safety and Effectiveness of Anti Inhibitor Coagulation Complex (AICC) in Routine Clinical Management: a Post-Authorization Safety Study (PASS)
Gingival Bleeding and Oral Hygiene in Women with von Willebrand Disease
Study Design of a Phase 3, Open-Label Trial of the Safety and Efficacy of Recombinant Factor IX Fc Fusion Protein for the Prevention and Treatment of Bleeding Episodes in Previously Untreated Patients With Severe Hemophilia B
Study Design of a Phase 3, Open-Label Trial of the Safety and Efficacy of Recombinant Factor VIII Fc Fusion Protein for the Prevention and Treatment of Bleeding Episodes in Previously Untreated Patients With Severe Hemophilia A
A Study Evaluating the Impact of myCubixx, an Innovative Factor Inventory Management and Storage System with Selected Outcomes on People with Hemophilia A
Safety of BAX 855, a Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) Conjugated Full-Length Recombinant Factor VIII Product
Extended-interval Dosing with rFIXFc Is Associated With Low Bleeding Rates and a Reduction in Weekly Factor Use
A Prospective Case-Control Study of Bleeding Phenotype in Hemophilia A Carriers
Dosing Routines and Bleeding Rates Before and Following Treatment with rFVIIIFc in the A-LONG Clinical Study
3-Year Results From SPINART: Prolonged Reduction of Bleeding With Prophylaxis Using Bayer’s Sucrose-Formulated Recombinant Factor VIII
Production and Characterization of BAX 855, PEGylated rFVIII with Extended Half-Life
SPINART Trial 3-Year Results With Bayer’s Sucrose-Formulated Recombinant Factor VIII: Improved Joint Function and Health-Related Quality of Life in Adults Using Prophylaxis
Joint Outcomes by Magnetic Resonance Imaging After Treatment With Bayer’s Sucrose-Formulated Recombinant Factor VIII in the SPINART Study: Results at the 3-year Evaluation Timepoint
Dosing Flexibility in Prophylaxis Regimens With Bayer’s Sucrose-Formulated Recombinant Factor VIII: Experience From Postmarketing Surveillance Studies
Objectives:
Factor VIII (FVIII) prophylaxis regimens for severe hemophilia A that allow more flexible dosing than the standard 3-times-weekly regimen while maintaining efficacy may improve adherence. This analysis compared the clinical efficacy of once- or twice-weekly versus ≥3-times-weekly prophylaxis dosing of Bayer’s sucrose-formulated recombinant FVIII (rFVIII-FS) in patients with severe hemophilia A.
Methods:
Data from 3 postmarketing studies were pooled. Patients with severe hemophilia A and no history of inhibitors who were receiving ≥1 prophylaxis infusion/wk of rFVIII-FS for ≥80% of a prophylaxis observation period (≥5 months) were included. Patients were categorized based on age (<18 and ≥18 years) and physician-assigned treatment regimens of 1–2 prophylaxis injections/wk (n=63) or ≥3 prophylaxis injections/wk (n=76). Descriptive statistics were determined for annualized bleeding rates (ABRs) by dosing group and age subgroups.
Summary:
Median (quartile 1; quartile 3) ABR for all bleeds was 2.0 (0; 4.0) in the group receiving 1–2 prophylaxis injections/wk and 3.9 (1.5; 9.3) in the group with ≥3 prophylaxis injections/wk. Similarly, median ABRs for joint, spontaneous, and trauma-related bleeds were numerically lower in the group receiving 1–2 prophylaxis injections/wk. The trend toward lower ABRs in the group with 1–2 prophylaxis injections/wk was observed in both age subgroups, although ABRs were somewhat higher in patients ≥18 vs <18 years. Zero annualized bleeds were reported by 30% and 7% of patients in the groups with 1–2 prophylaxis injections/wk and ≥3 prophylaxis injections/wk, respectively.
Conclusions:
These data demonstrate that bleeding control can be achieved in some patients with severe hemophilia A using a <3-times-weekly prophylaxis dosing regimen and that physicians’ judgment based on bleeding phenotype can successfully direct the frequency of prophylactic dosing.
Retrospective Database Analysis of the Prevalence of Cardiovascular Comorbidities in a US Patient Population with Hemophilia A: Confirmation of Findings
Global Assessment of Knowledge and Practices in the Diagnosis, Classification, and Management of Hemophilia among Pediatric Providers
Real-world Dosing Patterns of Factor in Hemophilia B Patients
Real-world dosing of factor in hemophilia A patients
Mobilizing Patients Towards Positive Health Management Through Motivational Interviewing
Objective:
Patient health outcomes are strongly correlated with management of their health condition. In chronic disease management, example hemophilia, a clinician often encounters situations where despite what the patient is instructed to do, there is resistance to follow directions, thus compromising the potential benefits of their treatment regimen.
The objective of these interventions was to test out motivational interviewing (MI) as an alternative communication approach to traditional advice -giving in especially difficult, yet common, hemophilia patient situations.
Methods:
Four case studies are reported, each with a different nurse, patient, and desired behavioral change. In each case study, the clinician had received education on the use of MI in health care settings. Multiple Tools and Paradigms were used with patients at different life stages, and in need of making changes in their self-care and disease management. The clinicians avoided traditional directive approaches and adopted collaborative methods that guided the patient to take responsibility for achieving their own health goals. Patients were followed post intervention to determine longevity of the success achieved through this intervention.
Results Summary:
In each case, the use of MI enabled the clinician to work collaboratively with the patient or caregiver, to evoke their own reasons for change, to elicit change planning, and to mobilize them towards healthier choices in managing their condition.
Case study 1: pediatric setting - Use of Engaging MicroskillsMicro skills (Open Questions, Affirmations, Reflections, Summaries) with a parent to empower their child to start self infusion.
Case study 2: pediatric setting - Use of MI Rulers to motivate an adolescent to choose a more appropriate sport activity.
Case study 3: Transition setting - Use of MI Spirit, especially partnership and honoring autonomy, with an adolescent.
Case study 4: Adult setting - Use of EPE (Elicit Provide Elicit Approach) with an adult who was not adherent to his prophylaxis regimen.
Conclusions:
MI was confirmed as a successful therapeutic approach with a variety of resilient clinical cases where traditional directive approaches had been unsuccessful. The use of MI created an open and trusted communication channel between the clinician and the patient or caregiver, concluding with a change plan agreement. Clinicians felt more fulfilled with their jobs and more satisfied with the result of their intervention. With appropriate education about this methodology, clinicians can use it with their patients where a behavioral change is required to achieve better therapeutic outcomes.
Identification of Previously Unreported F8 and F9 Gene Mutations in Hemophilia Subjects From the Phase 3 Clinical Trials of rFVIIIFc and rFIXFc
The effects of FXIa on clot formation and lysis in the thrombin generation assay
An Initiative to Implement Quality Improvement Measures for Hemophilia Treatment Centers
Safety and efficacy of a recombinant factor IX (BAX326*) in pediatric previously-treated patients with hemophilia B
Point-of-care musculoskeletal ultrasound is critical for the diagnosis of hemarthroses and soft tissue inflammation in adult patients with painful hemophilic arthropathy
Systematic review of clinical trials results assessing health-related quality of life in hemophilia patients receiving prophylaxis
Introduction and Objective:
Prospective clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of prophylaxis in reducing bleeding episodes in hemophilia A and B patients and those with inhibitors. However, data, predominantly from observational studies, have suggested more equivocal effects on health-related quality of life (HRQoL) [Buchbinder 2013]. The present review examined the impact of prophylaxis on HRQoL as measured during prospective trials.
Methods:
We conducted a systematic literature review of prospective studies evaluating the efficacy of prophylaxis in hemophilia using factor VIII, factor IX, or bypassing agents. Applying the inclusion criteria, we selected studies which evaluated HRQoL via validated instruments and summarized key data.
Results:
A total of 12 studies (hemophilia A [n=7]; hemophilia B [n=2]; inhibitors [n=3]) met all inclusion criteria and were reviewed. Of these studies, the investigational products were Advate (n=2), Kogenate (n=2), NovoEight (n=2), Eloctate (n=1), Rixubis (n=1), Aprolix (n=1), Feiba (n=2), and NovoSeven (n=1). HRQoL was assessed using one or a combination of the following instruments: SF-36 (n=3), EQ-5D (n=5), Haemo-QoL (n=2), Haem-A-QoL (n=3), Haemo-QOL-A (n=2) and general pain VAS (n=1). Seven of the 12 studies reported significant improvement in ≥1 HRQoL measure following prophylaxis. Advate, Rixubis and Feiba prophylaxis (among good responders with ≥ 50% bleed reduction) demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in the physical component and certain domain(s) scores of the SF-36 (Valentino 2012; Windyga 2013; Gringeri 2013). Additionally, prophylaxis with Feiba showed clinically meaningful and/or statistically significant improvements in HRQoL (EQ-5D, Haemo-A-QoL), general health status (EQ-VAS) and general pain scores (VAS) (Antunes 2014; Stasyshyn 2014). Although, a previous Kogenate study indicated non-significant change in HRQoL measures (Collins 2003), recently published results from the SPINART trial demonstrated statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in several domains of the Haemo-QoL-A (Hong 2014). Prophylaxis with Eloctate and Alprolix resulted in non-significant change in the HRQoL measures used in their respective trials (Wyrwich 2013). Statistical and clinical significance were not reported for prophylaxis treatment with NovoEight (Santagostino 2014). Prophylaxis with NovoSeven showed a non-significant trend towards improvement in all dimensions of the EQ-5D but statistical improvement in general health status (EQ-VAS) (Hoots 2008).
Conclusion:
Results from Advate, Kogenate, Rixubis and Feiba trials offer robust evidence of clinically and statistically significant improvement in HRQoL in hemophilia patients treated with prophylaxis.
Modelling the transfer of rFVIIa procoagulant signal from tissue factor to platelets
Hemophilia Inhibitor PUP Study (HIPS)
The Medical Home Neighbor: The Intermountain Hemophilia and Thrombosis Center’s Experience with Quality Improvement via the Children’s Health Improvement Collaborative Medical Home Demonstration Project in Utah
Depression in children with severe Hemophilia - a pilot study
Children with severe Hemophilia (CWH) suffer pain and inconvenience due to the required IV factor concentrates' injections and mostly exhibit poor quality of life. These children don't have any hope that their life will improve in the future. Most of them keep the Hemophilia a secret; therefore they are unable to get any emotional support from their peer group. These parameters are known stressors and triggers leading to depression, especially among children and adolescents (due to their lack of mature psychological defense mechanisms). The consequences of depression might be hazardous, since such children may neglect their medical treatment, leading to further deterioration of their medical state.
Objective:
We compared the depression level of children with Hemophilia to healthy children of the same age and background.
Methods:
Depression was evaluated using a standard validated questionnaire of depression that was developed by A.Beck - the CDI. We compared 20 children with severe Hemophilia with 25 non-Hemophiliac children.
Summary:
The calculated score for degree of depression was 7.6 for CWH vs age matched controls with a score of 12.32. The mean of normal populations is around 9. Parametrical T test for Equality of Means = 0.013.
This is the first reported study objectively addressing the issue of depression in CWH.
Conclusions:
We found the opposite of what we had expected: The children with Hemophilia were rated significantly much less depressed then the children without Hemophilia. This finding merits further validation in future larger studies and
must be examined very carefully, due to the complexity of the psychological defense mechanisms.
Kids A-LONG: Safety, Efficacy, and Pharmacokinetics of Long-Acting Recombinant Factor VIII Fc Fusion Protein (rFVIIIFc) in Previously Treated Children with Hemophilia A
Objective:
Kids A-LONG was a global, multi-center, open-label phase 3 study that evaluated the safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics (PK) of rFVIIIFc in previously treated patients aged <12 years with severe hemophilia A (<1 IU/dL FVIII activity).
Methods:
All participants had ≥50 prior exposure days (EDs) to FVIII, and no history of FVIII inhibitors. Participants were to be treated with twice-weekly rFVIIIFc prophylactic infusions (Day 1, 25 IU/kg; Day 4, 50 IU/kg), with adjustments to dose (≤80 IU/kg) and dosing interval (≥ every 2 days) as needed by the investigator. A subset of participants (<6 years of age, n=25; 6 to <12 years of age, n=35) underwent sequential PK evaluations with FVIII (50 IU/kg), followed by rFVIIIFc (50 IU/kg). The primary endpoint was development of inhibitors (neutralizing antibodies). Secondary endpoints included PK, annualized bleeding rate (ABR) and number of infusions required to control a bleed.
Summary:
The study enrolled 71 participants from 23 centers (<6 years, n=36; 6 to <12 years, n=35); 94.4% of participants completed the study. Prestudy, 89% of participants received FVIII prophylaxis, the majority (74.6%) of whom required ≥3 infusions per week. The median time on study for treated subjects (n=69) was 26 weeks; 61 participants had ≥50 EDs to rFVIIIFc. No participant developed inhibitors to rFVIIIFc. Overall, the pattern of adverse events reported on rFVIIIFc treatment was typical of the population studied; no serious adverse events were assessed as treatment-related by the investigator. The terminal half-life (arithmetic mean [95% CI]) in participants aged <6 years and 6 to <12 years was 12.67 (11.23, 14.11) hours and 14.88 (11.98, 17.77) hours, respectively. The relative increase in half-life over prior FVIII therapy was ~1.5-fold, consistent with the increase in half-life seen in the A-LONG study of adults and adolescents. Median (IQR) ABR was 1.96 (0.00, 3.96) overall, and 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) for spontaneous bleeds. Median total weekly dose and dosing interval were 88.1 IU/kg and 3.5 days, respectively. 83.7% and 93.0% of bleeding episodes were controlled with 1 or 1–2 infusions, respectively (median dose per bleeding episode: 54.9 IU/kg).
Conclusions:
rFVIIIFc was well-tolerated, efficacious for prophylaxis and treatment of bleeding, and resulted in low bleeding rates. The extended half-life compared to FVIII and the safety profile were generally consistent with that observed in the Phase 3 study in adults and adolescents. rFVIIIFc offers the potential of prolonged dosing intervals and fewer infusions for children with severe hemophilia A.
Home infusion/specialty pharmacy inhibitor management program leads to patient/provider collaboration to facilitate enhanced program and patient outcomes
Hemophilia of Georgia's Preventive Dental Program
Rates of falls, injurious falls, and activity restriction due to fear of falling in adults with hemophilia
Don’t Push Your Luck! Educational Board (not Bored) Game for Families Living with Hemophilia
Prevalence of Depression in US Patients with Hemophilia A Compared with a General Medical Population: A Retrospective Database Analysis
Pediatric Hemophilia and Post Trauma Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Patient, Caregiver, and Nurse Satisfaction with BAXJECT III, a Next-Generation Reconstitution System for AHF-rFVIII (ADVATE®)
FEIBA PROOF: A Prospective, open-label, randomized, parallel study with FEIBA NF to evaluate the efficacy and safety of prophylactic versus on-demand treatment in haemophilia A or B subjects with inhibitors
The PROLONG-ATE Study: A Phase 2/3 Study to Evaluate Efficacy and Safety of BAX 855,A Longer-Acting PEGylated Full-Length Recombinant Factor VIII (PEG-rFVIII),for Prophylaxis and Treatment of Bleeding in Severe Haemophilia A
A Phase I Study of Safety and Pharmacokinetics of BAX 855, a Longer Acting PEGylated Full-Length Recombinant Factor VIII (PEG-rFVIII), in Patients with Severe Hemophilia A
Outcomes of Total Knee and Hip Arthroplasty for Hemophilic Arthropathy
Relationship of quality of life, pain, and self-reported arthritis with age, employment, bleed rate, and utilization of hemophilia treatment center and healthcare provider services: US results from adult patients with hemophilia in the HERO study
Objective:
Examine potential relationships between health-related quality of life (QoL), pain interference and self-reported arthritis and age, employment, activity, bleed frequency, and hemophilia treatment center (HTC) and healthcare professional utilization within the HERO psychosocial assessment study.
Methods:
In HERO, adults with hemophilia (≥18 years) from 10 countries completed a 5-point Likert scale on pain interference over the prior 4 weeks, EQ-5D-3L (mobility, usual activities, self-care, pain/discomfort, anxiety/depression) and EQ-5D health-related visual analog scale (VAS, 0-100, coded as an 11-point categorical response). US responses are considered below.
Summary:
Of 675 adults, 189 (90 with self-reported arthritis) respondents were from the US. Adults with arthritis were older; median age also increased with progressive disability and worsening pain. The percentages reporting full-time, part-time, or self-employment and the percentage reporting “good” EQ-5D VAS scores of 80-90-100 declined with increasing disability and pain interference. Median number of annual bleeds increased with increasing disability, pain interference, and arthritis. There was little difference in the median number of HTC visits per year in those reporting pain or arthritis. The percentage of adults reporting a lot/extreme pain interference was higher in those with more disability and with arthritis. Adults with increasing pain interference and arthritis were more likely to report social worker and nurse involvement. Physiotherapist utilization decreased with increasing disability and arthritis.
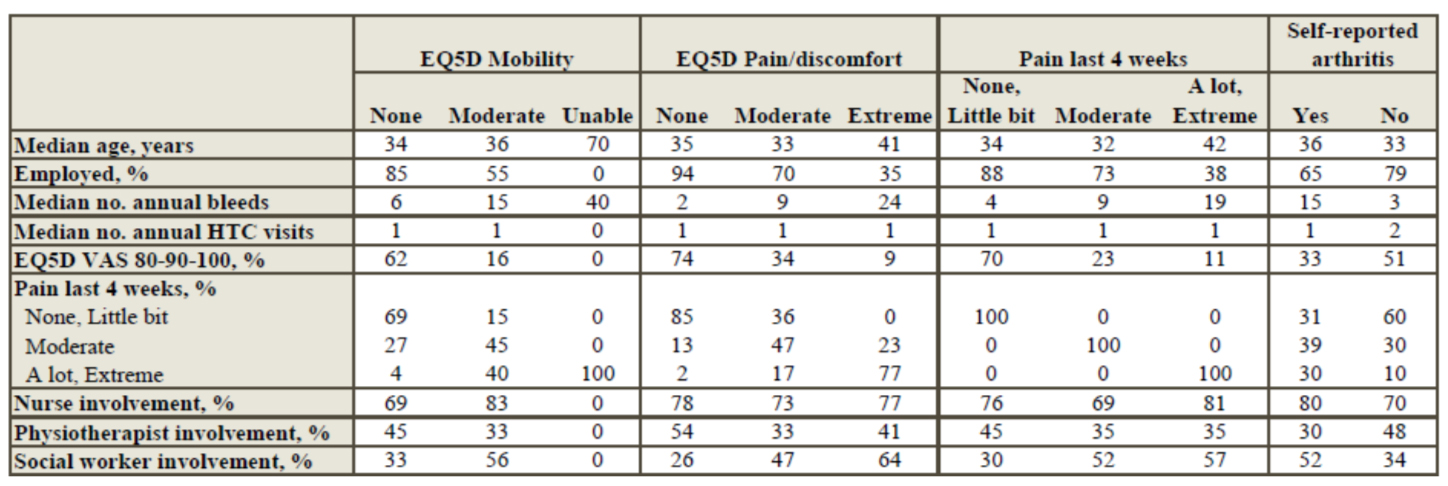
Conclusions:
In the US, increased disability and pain were associated with increased age, lower employment, higher reported bleed frequency, and lower QoL. Adults who reported experiencing more pain were more likely to report suffering from arthritis and more issues with mobility.
Atrial Fibrillation in People with Hemophilia: a Cross-Sectional Evaluation in Europe by the ADVANCE Working Group
Objective:
With increasing life expectancy of people with hemophilia (PWH) in developed countries, the number of PWH affected with age-related diseases is also increasing. Atrial fibrillation is a common health problem in the general population, but in PWH, evidence-based guidelines for the management of AF are lacking.
The aim of this cross-sectional pan-European study is to analyze the prevalence of AF and risk factors for stroke in our adult hemophilia population and to document current anticoagulation practice.
Methods:
The ADVANCE Working Group consists of members from 14 European hemophilia centers. Each center retrieved data on the number of PWH with AF in their hemophilia population, as well as their total number of adult PWH. For each person with AF, a case report form was completed.
Summary:
In total, 29 PWH with AF were documented. The mean age was 68.2 years (IQR 62-75.5). Hemophilia was severe in 6 (20.6%), moderate in 6 (20.6%) and mild in 17 (58.6%) patients. The prevalence in the total studied hemophilia population was 0.94% (29/3094) and increased with age; in patients >40 years it was 1.7% (29/1723) and in patients >60 years 3.6% (23/635). The mean CHA2DS2-Vasc score was 1.3 (IQR 0-2). Hypertension was reported in 12 patients (41.4%), diabetes in 3 (10.3%), previous stroke or TIA in 1 (3.4%), peripheral vascular disease in 4 (13.8%). In 11 patients (37.9%), anticoagulation was started of whom 9 low dose aspirin and 2 vitamin K antagonists. Of these 11 patients, 9 had mild hemophilia, 1 moderate and 1 severe with FVIII prophylaxis. During follow-up after diagnosis (mean follow-up 52.9 months), there were no thrombotic events reported, nor increases in bleeding severity.
Conclusions:
In this largest cohort of PWH with AF so far, the prevalence of AF in hemophilia increases with age and is predominantly present in mild hemophilia. Based on the population based CHA2DS2-Vasc risk scores, PWH have a low stroke risk that might be even lower considering the hypocoagulable state. Hemophilia doctors prescribe anticoagulation therapy approximately in half of their mild hemophilia patients and very few in moderate and severe.
Cardiovascular management in hemophilia: acute coronary syndromes – an assessment by the ADVANCE Working group on applicability of the ESC Guidelines
Prospective Study of Plasma-Derived Factor VIII/VWF in Immune Tolerance Induction Therapy: The Spirit Registry
Factor for Felons; Management of Incarcerated Hemophiliacs
Burden of Bleeding Episodes Among Persons With Hemophilia B
The use of Low Molecular Weight Heparins in Pregnancy: A single center experience 2002-2012
Prevalence and Predictors of Food Insecurity in Children with Hemophilia
Objectives:
The purpose of this pilot study was to quantify prevalence of food insecurity and determinants among households including children with hemophilia. Food insecurity, the limited or uncertain availability of nutritionally adequate and safe food, negatively affects children’s development and health. Households including people with hemophilia may be at increased risk for food insecurity due to hemophilia-related medical expenses and employment limitations.
Methods:
Food insecurity and health status, as assessed at annual comprehensive visits from May 2012-January 2013 were obtained by chart review. A two-question, validated screening tool was used to assess food insecurity status Descriptive statistics were applied to summarize participant characteristics. This study was approved by the Oregon Health & Science University Institutional Review Board.
Summary:
Data were available for forty-two male participants, aged 0-18 years, 42.9% had mild or moderate hemophilia and 57.1% severe. Prevalence of food insecurity overall was 16.7% (95% CI 5.4-28.0%), similar to national averages; food insecurity was rare among those with mild and moderate disease (5.6%) and concentrated among those with severe disease (25.0%; 95% CI 7.7-42.3%). Additionally, children who were older, taller, heavier, had higher body mass index (BMI) status, or were identified as a minority race or ethnicity were at increased risk for food insecurity (all P>0.05).
Conclusions:
This study provides pilot data showing the need for food insecurity screening and linkage to resources as a routine part of care, and the need for improved understanding of the determinants of food insecurity in this population.
B-LONG: Phase 3 Study of Long-Lasting Recombinant Factor IX Fc Fusion Protein (rFIXFc) in Hemophilia B
A-LONG: Phase 3 Study of Long-Lasting Recombinant Factor VIII Fc Fusion Protein (rFVIIIFc) in Hemophilia A
Preclinical Research with Recombinant Factor VIIa Fusion Proteins with Enhanced In vitro Activity and Improved Half-Life in Mice
H. Pylori as a cause of iron deficiency in children with bleeding disorders
Understanding the psychosocial undercurrents in spontaneous bleeds in severe hemophilia A to facilitate collaboration and customized/personalized regimens: a case study
Objective:
To examine the causes for spontaneous bleeds in severe hemophilia A patients on prophylaxis in an effort to increase care collaboration, decrease these incidents and optimize care.
Methods:
From our company’s bleeding disorders patients’ prescriptions and assessment records databases between April 1,2011 and March 31, 2012 (12 months period), prescriptions and assessment records were analyzed for prophylaxis (factor VIII) patients with severe hemophilia A who did not have inhibitors and who had at least one bleed (self- reported) requiring extra factor in the last 12 months. Due to limitations related to data retrieval from different databases, we eliminated all the patients where accuracy of match was doubtful resulting in a reduced “N”. Out of the 52 patients, 17 were identified with at least one spontaneous bleed. To identify details of psychosocial environment that might have contributed to the bleeds, chart reviews were done on five among them who reported two or more spontaneous bleeds.
Results:
Patients with four bleeds:
Patient A developed a left ankle target joint. Patient has not consistently reported bleeds to HTC. Specialty RPh notified HTC for evaluation of dose and to report bleed pattern.
Patient B frequently missed doses resulting in spontaneous bleeds.
Patients with three bleeds:
Patient C communicated well with home care and HTC. This collaboration contributed to care plan personalization and an increase in dose and frequency resulting in cessation of spontaneous bleeds.
Patients with two bleeds:
Patient D is a toddler making it difficult to identify spontaneous versus trauma induced bleeding. Homecare nurse communicated frequently with HTC leading to dosing adjustments resulting in rare spontaneous bleeds.
Patient E is a non-compliant teen and at times does not adhere to his prophy regimen.
Conclusion:
The goal of prophylaxis should be zero spontaneous bleeds. There are a variety of factors that might contribute to the bleeds such as lack of compliance, development of target joints, age, growth spurts, or improper dosing frequency and amount. Collaborating with a home infusion company or specialty pharmacy can afford an opportunity to identify and address some of these factors to take corrective actions wherever possible and hence to optimize outcomes.
Accommodating cultural needs and crossing language barriers in bleeding disorder patients: Results from a provider-patient survey by home infusion provider
Objective:
To demonstrate that providing homecare services to bleeding disorder patients with limited English proficiency in a culturally sensitive manner and in their native language can improve quality and outcomes of care.
Methods:
Provider and patient surveys were developed to measure the perceived value of interventions. Respondents were asked to rank dimensions of clarity of translated information, cultural sensitivity, satisfaction, and patient outcomes following homecare interventions on a scale of 1-9. Four patients from different ethnic backgrounds as well as their respective medical providers responded to a survey developed by the authors.
Results:
Our survey and its results, despite small numbers, demonstrate that patients as well as providers see value and improved outcomes when bilingual/bicultural professionals, interpreters and/or qualified translators were provided. Out of a total possible score of 9, an average score of 8.75 to 9 was obtained on the patient surveys. Patient respondents agreed that the information related to their treatment or care was provided in a language that was easy to understand and agreed the homecare service providers accommodated their cultural, religious or spiritual belief practices. Among the surveyed providers, services were ranked at an average of 8.75/9. The providers agreed that the language needs and cultural barriers of their patients were well addressed. It was reported that they “strongly believed” their patients “received accurate instruction on the prescribed treatment plan in a language that was easy for the patient/caregiver to understand” and addressing those needs “exceeded their expectations”.
Conclusion:
According to the Hemophilia Data Set (HDS) there has been a 236% increase in the Hispanic population and a 71% increase for other ethnic populations from 1990 to 2010. Our program has also seen a significant rise in the number of non-English speaking patients on service. This changing demographic landscape necessitates reform in the service delivery in terms of accommodating the needs of cultural diversity and overcoming language barriers. In order to do so, a continuous channel of communication is of high value to monitor and modulate changes in the population. Our survey and its results, demonstrate our success towards those ends, and hopefully will contribute to the continuous quality improvement (CQI) process in the provision of culturally competent care.
Specialty Pharmacy Educational Program, BE EMPOWERED, decreased joint bleeds in adults and increases RICE utilization among caregivers
Long-Term Follow-Up of Arteriovenous Fistulae in Bleeding Disorders
Prolonged factor IX expression after AAV-mediated gene transfer in adults with severe hemophilia B
Examining The Impact Of Parent Demographics, Child Characteristics And Child Hemophilia Related History On Parental Stress And Parent Support
Psychosocial Intervention To Improve Compliance with Comprehensive Care Visits
Objective:
Patients with hemophilia have been receiving comprehensive care at Hemophilia Treatment Centers (HTC) for the past 30 years which includes: annual medical and psychosocial assessments, training for home infusions of factor, physical therapy evaluations and treatment.
As many of our patients with Hemophilia now self -infuse, they require less visits to the HTC, Emergency Department and hospitalizations. We have noted over the past few years that many patients are delinquent in keeping yearly comprehensive visits. In an effort to increase attendance at comprehensive clinic, and introduce and assess the success of psychosocial interventions, on increasing compliance with appointments, a standard assessment form was created to identify reasons for non-attendance at comprehensive care visits.
Methods:
Data collection included characteristics of the household such as marital status and family size, last comprehensive re-evaluation and ages of patients (< 18 or >18 years). Assessment of barriers included: drug addiction, school related issues relating to academic success, value of comprehensive clinic during a non-emergent time, DYFS involvement, major psychosocial issues, transportation and work related issues such as financial concerns and concern for using days for non-emergent reasons.
Each identified patient was contacted by the social worker to assess reasons for non- compliance utilizing the standard assessment form. Following the assessment, the social worker created and implemented an individually tailored plan developing interventions and employing education, counseling and supportive services.
Summary:
A total of 26 patients were identified as delinquent in comprehensive care visits. Eight were pediatric patients and eighteen were adult patients. All identified patients were called and assessed for barriers to compliance with clinic visits. The major barrier identified was both parents’ and patients’ value of comprehensive clinic during a non-emergent time (46 % of patients). The second major barrier was work related issues (31% of noncompliance). Major psychosocial issues (15 %) and school issues (8 %) accounted for the remaining causes of non-compliance with clinic appointments. Individual plans to address barriers were made and implemented. Following the psychosocial intervention 46 % of the previously non- compliant patients made comprehensive clinic visits.
Conclusions:
Identification of psychosocial reasons for non-compliance to comprehensive care clinic with the development of individual plans to address needs lead to improved compliance with visits.
Biodistribution of rVIIa-FP, a Recombinant Fusion Protein Linking Coagulation Factor VIIa With Albumin, in Rats
Great Plains Regional Girls with Bleeding and Clotting Disorders Camp
Effect of Albumin Fusion on the Biodistribution of Recombinant Factor IX-FP
The National Hemophilia Program Coordinating Center - Assessing Support Needs of HTC Staff
Dosing intervals and bleeding rates before and following treatment with recombinant Factor IX Fc fusion protein in patients with severe hemophilia B: Experience from the B-LONG study
Adherence and outcomes in hemophilia
Objective:
Adherence to treatment has an important impact on health outcomes in chronic conditions, but the relationship between adherence to prophylactic infusions and outcomes in hemophilia is not well documented. This study was conducted to assess the relationship between adherence to prophylaxis and outcomes, including patient-reported health status and bleeding.
Methods:
Adults with hemophilia and parents of minors with hemophilia were identified through a panel of patients originally recruited from hemophilia treatment centres and associations. Panelists reporting moderate or severe hemophilia completed an on-line questionnaire, which included the Validated Hemophilia Regimen Treatment Adherence Scale-Prophylaxis (VERITAS-Pro) for adherence to prophylactic treatment, a measure of health status (adults: SF-12v2 questionnaire; parents of pediatric patients: SF-10) and items assessing the number of times they experienced clinical outcomes, such as breakthrough bleeds, ER visits, hospital admissions, and missed days from work/school due to bleeding episodes. All measures were through self- or parent-report. Generalized linear models were used to assess the relationship between adherence and outcomes, adjusting for age (adults only). The protocol and questionnaire were approved by an institutional review board and all respondents provided informed consent.
Summary (of results obtained):
A total of 53 adults with hemophilia A (n=43) or B (n=10) treated with prophylaxis completed the survey and provided age information. In analyses combining these groups, lower adherence was associated with more days of work or school missed due to bleeding episodes in the past year (p<0.05), as well as the number of bleeding episodes requiring administration of replacement factor in the past year (p<0.001). The relationship between adherence and bleeding episodes was also significant in analyses separating A and B patients (p<0.01 and p<0.05, respectively), as was the link between adherence and days missed in hemophilia A (p<0.05). Adherence was not significantly associated with physical health status (p=0.91) among adults. Among pediatric patients treated with prophylaxis (n=56), the relationship between adherence and number of bleeding episodes in the past year was not significant (p= 0.95). Adherence was associated with clinical outcomes related to bleeding episodes over the past year, such as infection at the injection site (p<0.05), hospital stay due to bleeding episodes (p<0.001), and missed days from work/school due to bleeding episodes (p<0.01). Furthermore, physical health status was better among more-adherent pediatric patients (p<0.01).
Conclusions:
Though sample sizes were limited, greater adherence to prophylaxis was associated with better self-reported clinical outcomes among both adult and pediatric hemophilia patients.
Relative importance of treatment characteristics to patients and parents of children with hemophilia
Preclinical Characteristics of a Recombinant Fusion Protein Linking Activated Coagulation Factor VII With Albumin (rVIIa-FP)
Preclinical PK/PD Characteristics of rVIII-SingleChain, a Novel Recombinant Single-Chain FVIII
Characterization of the Binding of a Novel Recombinant Single-Chain FVIII to von Willebrand Factor
Objective:
The binding behavior of rVIII-SingleChain to plasma-derived von Willebrand Factor (pdVWF) was assessed in surface plasmon resonance (SPR) studies.
Methods:
The purification of VWF from human plasma–yielded pdVWF free of factor VIII (FVIII). Subsequently, isolated pdVWF was immobilized on a SPR gold chip using monoclonal antibodies (MAbs). Thereafter, the binding behavior of rVIII-SingleChain and full-length rFVIII molecules were studied and binding kinetics were calculated. Regeneration of pd-VWF was performed with calcium chloride, while regeneration of the covalently coupled anti-VWF MAbs was achieved in the presence of an acidic pH.
Summary:
The affinity of CSL Behring’s rVIII-SingleChain to pdVWF was significantly higher than those of commercially available rFVIII full-length molecules. The higher affinity was derived from a higher association rate constant, while the dissociation rate constants were comparable. Intriguingly, the higher affinity had no influence on other functional characteristics of rVIII-SingleChain (eg, the binding to phospholipids, thrombin generation capacity, and FVIII enzymatic activity were comparable to full-length rFVIII). The results obtained from the SPR studies in vitro appear consistent with the observation of improved pharmacokinetic characteristics for rVIII-SingleChain in comparison to full-length rFVIII. After treatment of hemophilia A mice with single doses of rVIII-SingleChain or full-length rFVIII, the systemic availability and mean residence time were found to be increased for rVIII- SingleChain compared to full-length rFVIII. In addition, a decreased clearance rate and an enhanced terminal half-life were observed for rVIII-SingleChain, while in vivo recovery and volume of distribution of rVIII-SingleChain were comparable to full-length rFVIII.
Conclusion:
Overall, it seems conceivable that the higher affinity of CSLB’s rVIII-SingleChain to pdVWF may have a positive effect on its systemic availability by a delayed elimination from plasma.
Motivational Interviewing and Health Behavior Change: An Educational Intervention for Healthcare Professionals
The influence of co-morbidities on annualized bleeding rates in patients with severe hemophilia A: experiences from the pivotal turoctocog alfa prophylaxis trial (guardianTM1)
Overview of a global clinical trial program with turoctocog alfa, a new recombinant factor VIII: the guardian™ program
Turoctocog alfa, a new B-domain truncated, recombinant factor VIII (rFVIII) developed by Novo Nordisk for the prevention and treatment of bleeding episodes in hemophilia A patients
Prospective Clinical Trial of a Novel Recombinant Factor IX in Previously Treated Patients
Objective:
This prospective clinical trial was conducted to assess the safety, efficacy and PK of BAX326 (a novel recombinant FIX [rFIX] manufactured without the addition of any materials of human or animal origin, and with two viral inactivation steps [solvent/detergent treatment and nanofiltration]) in previously-treated patients aged 12 to 65 with severe (FIX level < 1%) or moderately severe (FIX level ≤ 2%) hemophilia B.
Methods:
Hemostatic efficacy after twice weekly prophylaxis with BAX326 was determined in terms of annualized bleeding rate (ABR) compared with a historical control group treated on- demand. PK equivalence was assessed between BAX326 and a commercial rFIX in a crossover design. Safety was evaluated by the occurrence of adverse events.
Summary:
In subjects on twice weekly prophylaxis with BAX326 over at least 3 months (N=56), 24 (43%) did not bleed throughout the study observation period, and the ABR was substantially lower when compared with a historical control group (79% reduction, p<0.001). Joint bleeds (major joints: wrist, elbow, shoulder, hip, knee, ankle) occurred at a mean ABR of 2.85 ± 4.25 compared with 1.41 ± 2.87 in non-joint bleed sites. Of the 32/56 subjects with bleeds, 90.6% (29/32) had arthropathy at screening and only 28.1% (9/32) did not have target joints, as compared to subjects without bleeds, of whom 79.2% (19/24) had arthropathy and 50% (12/24) did not have target joints at screening. Higher mean ABRs were observed in subjects with arthropathy (N=46) versus without arthropathy (N=8) (4.54 vs. 2.57 for all bleeds, 3.16 vs. 1.02 for joint bleeds, and 1.97 vs. 0.25 for spontaneous bleeds). A similar pattern was observed for the ABRs of joint bleeds and spontaneous bleeds in subjects with target joints (N=35) (mean ABR: 2.41 ± 3.79) and those with no target joints (N=21) (mean ABR: 0.58 ± 1.63). Most bleeds were controlled with 1-2 infusions of BAX326 and with an efficacy rating of “excellent.” BAX326 was equivalent to the comparator rFIX in terms of AUC 0 72 h /dose. BAX326 is safe and well tolerated in hemophilia B patients, with no signs of immunogenicity or thrombotic events.
Conclusions:
BAX326 has a positive safety profile and is efficacious in treating bleeds and in routine prophylaxis in PTPs aged ≥12 years with hemophilia B. The results also demonstrate that subjects with target joints and hemophilic arthropathy receiving secondary prophylaxis tend to have higher ABRs as compared to those without these underlying conditions.
Efficacy and safety of a novel rFIX (BAX326): phase III study in previously treated patients with severe or moderately severe hemophilia B undergoing surgical or other invasive procedures
Reduced Joint Range of Motion in Females with FVIII Deficiency
Collaborative partnership helps resolve cultural barriers in patient receiving continuous infusion of factor (ACAT Protocol) in the home setting
Objective:
When a surgical procedure is required in a patient with hemophilia, continuous infusion of factor (CIF) is a safe and effective alternative to bolus dosing.1-5 However, when cultural values collide with best practices, a patient-centered collaborative care plan is necessary to help ensure a positive outcome while respecting the core values of the patient.
Method:
Our team collaborated with our local Hemophilia Treatment Center (HTC) physicians and nurses to plan CIF for an Amish patient who required a total knee replacement. After interviewing the patient, the care team recognized when the patient transitioned on CIF to the home, we would need to respect the cultural beliefs of the patient without compromising the care.
The HTC physician and nurse ordered continuous infusion of factor for the patient with goal factor levels to remain between 70-100% on post-op days 1-7 and between 50-70% on post- op days 8-14. The home infusion team collaborated with the family and HTC team to finalize the care plan. The patient-centered decision prompted the use of a battery powered ambulatory infusion pump and the use of pre-approved sliding scale factor orders (ACAT protocol) with daily factor levels. Our biggest barrier was in respect to communication with the patient. In our local Amish community, telephones are not accessible. Our brainstorming lead to our COO suggesting we include a battery operated phone that would be attached to the pump and only be used for pump emergencies.
Summary:
The patient was discharged to home post-op day three with recombinant factor VIII running at 2.5 units/kg/hour via a battery operated ambulatory pump. Levels on post-op day four were below 70, prompting the nurse to call on the “pump phone” and return for a visit that night to increase the rate to 2.7 units/kg/hour. The rate remained the same throughout the remainder of the therapy and the levels stayed within the range designated by the physician.
Conclusion:
The patient-centered multidisciplinary care plan allowed for a positive outcome while respecting the patient’s culture.
Better Adherence to Prescribed Treatment Regimen is Associated with Less Chronic Pain among Adolescent and Young Adults with Moderate or Severe Hemophilia
Background/Aim:
Little data exist, especially for adolescents and young adults (AYAs), about the relationship between adherence to prescribed hemophilia treatment regimens and chronic pain (CP).
Methods:
A convenience sample of hemophiliacs aged 13-25 completed an IRB-approved, online survey addressing regimen-specific adherence and CP between April through December of 2012. Adherence was assessed for prophylactic (VERITAS-Pro) and on- demand (VERITAS-PRN) participants. VERITAS scores range from 24 (most adherent) to 120 (least adherent). CP was measured using the revised Faces Pain Scale (FPS-R). CP was dichotomized as high (‘moderate’ to ‘worst pain possible,’ i.e., ≥4) or low (‘mild’ or ‘no pain,’ (i.e., <4). Multivariable, parsimonious logistic regression models assessed factors associated with high vs low CP levels. Separate models were constructed to evaluate a combined VERITAS score among prophylactic and on-demand patients and the VERITAS- Pro score among prophylactic patients only. Small sample size precluded analysis of on- demand (only) participants.
Results:
Ninety-three AYAs participated. Mild patients (n=13) were excluded. Of the remaining 80 participants (79 male), 91% had severe disease, 86% infused prophylactically, and 91% had Hemophilia A. Fifty-one percent were aged 13-17, most were white (76%), non- Hispanic (88%), and never married (93%). The majority (94%) had some type of health insurance.
Mean VERITAS-Pro (n=69) and PRN (n=11) scores were 49.6 ±12.9 (range 25-78) and 51.0 ±11.6 (range 35-74), respectively. CP was reported as high for 35% of respondents (36% for prophylactic vs 27% for on-demand, p=.74). Mean VERITAS-Pro scores for those with high and low CP were 53.6 ±12.3 vs 47.4 ±12.9, p=.05. VERITAS-PRN scores were similar across CP status. Logistic regression analysis revealed that for each 10-point reduction (increase in adherence) in the combined VERITAS score (Pro and PRN) there was a 35% (OR=0.65; 95%CI=0.44, 0.96; p=.03) reduction in the odds of having high CP. Among prophylactic respondents: for each 10-point reduction in the VERITAS-Pro score there was a 39% (OR=0.61; 95%CI=0.39, 0.96; p=.03) reduction in the odds of having high CP and compared to whites, non-whites were 4.42 (95%CI: 1.21, 16.1; p=.02) times as likely to report high CP.
Oral Care for People with Von Willebrand Disease: An Unmet Need
Speaking Frankly to Young Adults with Hemophilia
Objective:
Few online resources are available for teens and young adults living with hemophilia. Frankly.net aspires to serve as a candid, trusted resource on real issues of concern for this age group. Our online forum provides news, tips and information to help young adults with hemophilia live the lives they choose.
Method:
In 2008, an editorial board was established to guide the creation of Frankly.net, an online magazine targeting young men with hemophilia. Board members include experts in the areas of healthcare, social work and advocacy, and two are young men living with hemophilia.
Frankly.net content is controlled exclusively by the editorial board and sponsored by Bayer Healthcare with the goal of casting light on often taboo subjects within the community, such as sexuality, drugs and depression. An editorial calendar is maintained to ensure fresh content is published regularly.
Frankly.net is mobile-optimized and includes rich video content. Users are encouraged to keep up with the latest content by following @FranklyNet on Twitter.
Summary:
Since its inception, the editorial board has guided the creation of more than 80 stories. Articles include topics that resonate with young adults such as travel, entertainment, relationships and sex. Engaging video stories are also available in English and Spanish.
To date, Frankly.net has seen nearly 7,500 visitors from more than 125 countries across the globe, including the US, India, Germany, Canada.
In 2013, Frankly.net underwent a site makeover, re-launching with a new look and feel. Plans to further engage with an international audience are also underway. Korea launched a fully translated site in early 2013 under the guidance of a Korean editorial board. A Latin American version is in development and content from the site has been repurposed and translated in a dozen countries.
Conclusions:
Frankly.net is a unique resource for teenagers and young adults with hemophilia around the world. It continues to push boundaries as a way to help young men navigate the ups and downs of living with hemophilia.
Determining the impact of instrument variation and automated software algorithms on the thrombin generation test under hemophilia treatment conditions
Predicting PK/PD advantages of modified activated coagulation factor VII molecules
Stepping Up and Reaching Out to the Community
Objective:
Who better to understand and help advocate for the bleeding disorders community than those who live it every day? Step Up Reach Out (SURO) was created to help foster the next generation of leaders in the bleeding disorders community.
Method:
SURO is an international leadership program designed to help build tomorrow's leaders in the bleeding disorders community. The program was created by the University of Texas Health Science Center, Gulf States Hemophilia and Thrombophilia Center (UTHS) in 2007 with support from Bayer HealthCare.
SURO brings together young people (18-24 years old) from around the world for learning, personal growth and collaboration. This one-year program consists of two sessions of leadership training, activities focused on developing communications skills, and individual and group projects. During the time between the two sessions, participants are asked to identify an area in their communities for which they would like to step up and define an action plan, putting into practice the skills they have acquired. They continue to learn from and support one another through the SURO Alumni Network.
Summary:
To date, the SURO program has trained nearly 100 individuals from more than 20 countries, ranging from the US to Mexico, India and beyond. SURO alumni have come out of the program ready to put their action plans to the test, developing programming to support their local community needs.
Conclusions:
SURO helps participants build self-esteem, develop concrete thinking abilities and make decisions that will help make them become leaders in their own right.
Translation and Validation of an Instrument to Measure the Care-related Quality of Life of Informal Caregivers in English for the United States
Objective:
Caregivers of hemophilia patients may experience physical, social, emotional and financial problems as a result of their care tasks. Measurement of the caregiver experience is important in hemophilia as the majority are informal caregivers; typically unpaid family or friends. In order to carry out studies within the United States, a need exists for a translated and validated instrument to measure informal caregivers’ care-related quality of life in English for the U.S.
Methods:
The CarerQol instrument, covering 7 domains measuring the care-related quality of life of informal caregivers, including fulfillment, relational, mental and physical health problems, social impact, receipt of family support and financial impact, was selected on which to base an English U.S. version. The Dutch (Netherlands) source was translated into English (U.S.) by two forward linguists, working independently, who then collaborated to create a harmonized version. The project team, consisting of the forward translators, project manager, survey research analyst and independent Dutch (Netherlands) reviewer, discussed the harmonized English (U.S.) version to make necessary revisions. The English (U.S.) harmonization was then back-translated into Dutch (Netherlands), and a second Dutch linguist compared the back-translation to the source Dutch to ensure conceptual equivalence of the English forward translation and Dutch source. A client representative, who is a native English (U.S.) speaker, reviewed the English translation against the Dutch as an additional quality measure. After the English (U.S.) harmonization was finalized, it was debriefed via telephone interviews with 5 volunteers using screenshots of the questionnaire’s web version.
Summary:
A total of 5 subjects from the U.S. participated in debriefing interviews. Subjects ranged in age from 24 to 59 years, with educational levels ranging from 11 to 16 years. Sixty percent (60%) of the sample was female. Interview data confirmed that the English (U.S.) harmonized translation is conceptually equivalent to the source Dutch, and is understood by subjects in the United States.
Conclusion:
Per the cognitive debriefing results, the English (U.S.) harmonized translation based on the Dutch CarerQol instrument adequately captures the concepts in the original Dutch and, overall, is easily understood and confirmed as culturally appropriate by subjects in the United States. The resulting instrument is validated for use by English speakers in the United States, and captures the 7 quality of life domains as included in the source instrument.
Efficacy of a strength training program for improving elbow joint range of motion and function in adults with hemophilia
Successful buffalo hump removal using liposuction in two men with severe hemophilia and HIV
Canadian social worker and nurse perspectives on the Hemophilia Experiences, Results and Opportunities (HERO) study results from Canada
Clinical Study to Investigate the Immunogenicity, Efficacy and Safety of Treatment with Human-cl rhFVIII in Previously Untreated Patients with Severe Haemophilia A
Results of a prospective, non-interventional clinical study in 170 VWD patients with a new generation of VWF/FVIII concentrate in Germany
Clinical Study in Children with Severe Haemophilia A Investigating Efficacy, Immunogenicity, Pharmacokinetics, and Safety of Human-cl rhFVIII
Use of a double virally inactivated FVIII/VWF in 30 children and young people with von Willebrands disease - a single centre experience
Global Development Plan for a Double Virus Inactivated Fibrinogen Concentrate for the Treatment of Congenital Fibrinogen Deficiency
Patients’ and Caregivers’ Perspectives on Stability of Factor VIII Products for Hemophilia A: A Web-Based Study in the United States and Canada
Pathogen Safety of Plasma-Derived Clotting Factor Concentrates Demonstrated by Validation of Inactivation and Removal Steps in the Manufacturing Process
Objective:
To assure plasma-derived clotting factor concentrates are pathogen safe, virus inactivation and removal methods are applied to the manufacturing process. The effectiveness of currently used methods and procedures was demonstrated.
Methods:
The virus reduction capacity of the manufacturing process for a specific product was quantitated for selected steps of the manufacturing process. A prerequisite of such virus validation studies is a valid downscaling of the manufacturing process to a laboratory scale. After spiking product intermediates with a panel of viruses the same as or similar to known and emerging pathogens, the manufacturing steps were performed according to the defined procedures and the reduction factors for the different viruses measured. Prion reduction was also studied, employing both a microsomal preparation (membrane-associated prions) and purified prion protein. Methods in the manufacturing process solely for the purpose of pathogen reduction, such as pasteurization, solvent-detergent treatment, dry heat treatment of the final container, and virus (nano) filtration, as well as manufacturing steps for purification and concentration of the desired protein(s) such as partitioning by precipitation or chromatography, were studied. The residual risk of transmitting pathogens was assessed based on the results of these studies and the potential virus load in the plasma pool used to produce these products.
Summary:
For a pasteurized FVIII/vWF concentrate, the overall log reduction factors were ≥10.2 for HIV, ≥11.7 for BVDV, 10.2 for PRV, 7.8 for HAV, and 6.0 for CPV, as well as 6.4 and 7.9 for the 2 prion preparations, respectively. For a FVIII/vWF concentrate using solvent- detergent and dry heat, values were ≥12.5 for HIV, ≥13.1 for BVDV, ≥11.4 for PRV, ≥12.2 for HAV, and 6.7 for parvoviruses, as well as 4.0 and 4.9 for the 2 prion preparations. For a FIX concentrate using affinity chromatography and virus filtration, values were ≥10.2 for HIV, ≥12.6 for BVDV, ≥12.8 for WNV, ≥16.1 for PRV, ≥6.7 for HAV, and ≥14.8 for parvoviruses. For a FXIII concentrate using adsorption, chromatography, heat treatment, and virus filtration, values were ≥10.2 for HIV, ≥12.6 for BVDV, ≥12.8 for WNV, ≥16.1 for PRV, ≥6.7 for HAV, and ≥14.8 for parvoviruses, as well as 9.6 and 9.7 for the 2 prion preparations.
Conclusions:
Pathogen safety is based on the overall pathogen reduction factor considerably exceeding the amount of pathogen potentially entering the manufacturing pool. Validation studies verify that safety is attained for currently manufactured plasma-derived clotting factor concentrates.
Assuring the Virus Safety of Source Plasma for Further Manufacturing by Establishing Epidemiological Limits in Donor Centers
Low inhibitor incidence in previously untreated patients with severe haemophilia A treated with octanate® - Update from the PUP-GCP clinical trial
Characteristics and Treatment Patterns of Medicaid Patients with Hemophilia A Receiving Prophylaxis vs. On-Demand Factor VIII Therapy
Objective:
Few data sources contain sufficient patient count to study the real-world efficacy of factor VIII (FVIII) therapy in patients with hemophilia A (HA). Health insurance claims databases offer that opportunity. This study sought to identify patients with HA receiving prophylaxis versus on-demand FVIII regimens and describe their characteristics and treatment patterns utilizing data from Medicaid programs.
Methods:
Healthcare claims from Florida, Iowa, Kansas, New Jersey, and Missouri Medicaid programs covering 1996 to 2011 were used. Patients with ≥2 HA diagnoses (ICD-9 286.0), ≥2 dispensings for FVIII after age 2, continuous Medicaid eligibility ≥6 months before (baseline period) and ≥12 months after the first FVIII fill, and no evidence of bypassing agents or desmopressin use were included. Prophylaxis and on-demand regimens were identified using an algorithm calibrated to distinguish the regimens within five age groups based on the annual total units of FVIII dispensed regardless of the severity level: 16,480 IU (2–7 years old); 32,770 IU (8–12); 66,920 IU (12–16); 98,349 IU (17–21); 204,552 IU (≥22). The algorithm was developed using prescription records of 1,311 patients from three U.S. specialty pharmacy databases. FVIII treatment patterns and patient demographic and clinical characteristics were examined.
Summary:
From the approximately 14.8 million covered lives encompassed in the five Medicaid databases, a total of 2,408 (0.016%) patients with ≥2 diagnoses for HA were identified; 448 met the study eligibility criteria with 229 (51.1%) patients receiving prophylaxis FVIII and 219 (48.9%) patients receiving on-demand FVIII. Younger patients were more likely to receive prophylaxis therapy (percent by age group: 61% [2–7]; 70% [8–12]; 63% [12–16]; 51% [17–21]; 20% [22+], mean (SD) age, prophylaxis: 10.8 (9.8) years old; on-demand: 18.7 (14.4) years old). Mean (range) observation period was 5.6 (1.0-15.2) years for prophylaxis patients and 5.6 (1.0-15.2) years for on-demand patients.
Conclusions:
In a population of 448 Medicaid patients with HA, this study found that 51.1% and 48.9% patients received prophylaxis and on-demand FVIII regimens, respectively. With the average observation of patients for more than 5.5 years, this database offers the potential for long-term follow-up to assess the relative efficacy of prophylaxis versus on-demand FVIII regimens in decreasing the incidence of bleeding events. These evidences from claims databases are critical to payers and decision makers as they reflect real-world clinical practice and patterns of FVIII use. Information on HA severity level was not available in the databases used.

